Nuclear import of the yeast hexokinase 2 protein requires α/β-importin-dependent pathway
- PMID: 22157003
- PMCID: PMC3271005
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.317230
Nuclear import of the yeast hexokinase 2 protein requires α/β-importin-dependent pathway
Abstract
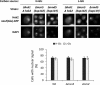
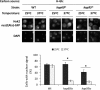
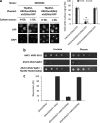
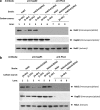
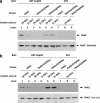
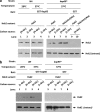
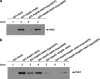
Hexokinase 2 (Hxk2) from Saccharomyces cerevisiae was one of the first metabolic enzymes described as a multifunctional protein. Hxk2 has a double subcellular localization and role, it functions as a glycolytic enzyme in the cytoplasm and as a regulator of gene transcription of several Mig1-regulated genes in the nucleus. However, the mechanism by which Hxk2 enters in the nucleus was unknown until now. Here, we report that the Hxk2 protein is an import substrate of the carriers α-importin (Kap60 in yeast) and β-importin (Kap95 in yeast). We also show that the Hxk2 nuclear import and the binding of Hxk2 with Kap60 are glucose-dependent and involve one lysine-rich nuclear localization sequence (NLS), located between lysine 6 and lysine 12. Moreover, Kap95 facilitates the recognition of the Hxk2 NLS1 motif by Kap60 and both importins are essential for Hxk2 nuclear import. It is also demonstrated that Hxk2 nuclear import and its binding to Kap95 and Kap60 depend on the Gsp1-GTP/GDP protein levels. Thus, our study uncovers Hxk2 as a new cargo for the α/β-importin pathway of S. cerevisiae.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Yeast importin-β is required for nuclear import of the Mig2 repressor.BMC Cell Biol. 2012 Nov 6;13:31. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-13-31. BMC Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 23131016 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear export of the yeast hexokinase 2 protein requires the Xpo1 (Crm1)-dependent pathway.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jul 31;284(31):20548-55. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.013730. Epub 2009 Jun 12. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19525230 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear import of dimerized ribosomal protein Rps3 in complex with its chaperone Yar1.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 7;6:36714. doi: 10.1038/srep36714. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27819319 Free PMC article.
-
Classical nuclear localization signals: definition, function, and interaction with importin alpha.J Biol Chem. 2007 Feb 23;282(8):5101-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R600026200. Epub 2006 Dec 14. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17170104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The hexokinase 2-dependent glucose signal transduction pathway of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2002 Mar;26(1):83-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2002.tb00600.x. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2002. PMID: 12007644 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein kinase Ymr291w/Tda1 is essential for glucose signaling in saccharomyces cerevisiae on the level of hexokinase isoenzyme ScHxk2 phosphorylation*.J Biol Chem. 2015 Mar 6;290(10):6243-55. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.595074. Epub 2015 Jan 15. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25593311 Free PMC article.
-
The function of importin β1 is conserved in eukaryotes but the substrates may vary in organisms.Plant Signal Behav. 2013 Aug;8(8):e25106. doi: 10.4161/psb.25106. Epub 2013 Jun 3. Plant Signal Behav. 2013. PMID: 23733071 Free PMC article.
-
Candida albicans Hexokinase 2 Challenges the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Moonlight Protein Model.Microorganisms. 2021 Apr 15;9(4):848. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9040848. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33920979 Free PMC article.
-
Hexokinase 2 Is an Intracellular Glucose Sensor of Yeast Cells That Maintains the Structure and Activity of Mig1 Protein Repressor Complex.J Biol Chem. 2016 Apr 1;291(14):7267-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.711408. Epub 2016 Feb 10. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26865637 Free PMC article.
-
Moonlighting Proteins: The Case of the Hexokinases.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Jun 9;8:701975. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.701975. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34235183 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Görlich D., Prehn S., Laskey R. A., Hartmann E. (1994) Isolation of a protein that is essential for the first step of nuclear protein import. Cell 79, 767–778 - PubMed
-
- Stade K., Ford C. S., Guthrie C., Weis K. (1997) Exportin 1 (Crm1p) is an essential nuclear export factor. Cell 90, 1041–1050 - PubMed
-
- Weis K. (2003) Regulating access to the genome. Nucleocytoplasmic transport throughout the cell cycle. Cell 112, 441–451 - PubMed
-
- Kalab P., Weis K., Heald R. (2002) Visualization of a Ran-GTP gradient in interphase and mitotic Xenopus egg extracts. Science 295, 2452–2456 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

