Mechanoinduction of lymph vessel expansion
- PMID: 22157817
- PMCID: PMC3280555
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2011.456
Mechanoinduction of lymph vessel expansion
Abstract
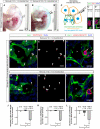
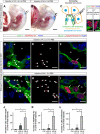
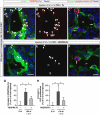
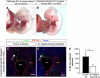
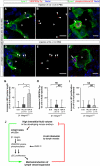
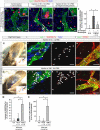
In the mammalian embryo, few mechanical signals have been identified to influence organ development and function. Here, we report that an increase in the volume of interstitial or extracellular fluid mechanically induces growth of an organ system, that is, the lymphatic vasculature. We first demonstrate that lymph vessel expansion in the developing mouse embryo correlates with a peak in interstitial fluid pressure and lymphatic endothelial cell (LEC) elongation. In 'loss-of-fluid' experiments, we then show that aspiration of interstitial fluid reduces the length of LECs, decreases tyrosine phosphorylation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 (VEGFR3), and inhibits LEC proliferation. Conversely, in 'gain-of-fluid' experiments, increasing the amount of interstitial fluid elongates the LECs, and increases both VEGFR3 phosphorylation and LEC proliferation. Finally, we provide genetic evidence that β1 integrins are required for the proliferative response of LECs to both fluid accumulation and cell stretching and, therefore, are necessary for lymphatic vessel expansion and fluid drainage. Thus, we propose a new and physiologically relevant mode of VEGFR3 activation, which is based on mechanotransduction and is essential for normal development and fluid homeostasis in a mammalian embryo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Comment in
-
Lymphatics thrive on stress: mechanical force in lymphatic development.EMBO J. 2012 Feb 15;31(4):781-2. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.484. Epub 2012 Feb 15. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22334045 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Affolter M, Zeller R, Caussinus E (2009) Tissue remodelling through branching morphogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10: 831–842 - PubMed
-
- Bahram F, Claesson-Welsh L (2010) VEGF-mediated signal transduction in lymphatic endothelial cells. Pathophysiology 17: 253–261 - PubMed
-
- Calvo CF, Fontaine RH, Soueid J, Tammela T, Makinen T, Alfaro-Cervello C, Bonnaud F, Miguez A, Benhaim L, Xu Y, Barallobre MJ, Moutkine I, Lyytikkä J, Tatlisumak T, Pytowski B, Zalc B, Richardson W, Kessaris N, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Alitalo K et al. (2011) Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 directly regulates murine neurogenesis. Genes Dev 25: 831–844 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

