The RPT2 subunit of the 26S proteasome directs complex assembly, histone dynamics, and gametophyte and sporophyte development in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 22158466
- PMCID: PMC3269867
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.111.089482
The RPT2 subunit of the 26S proteasome directs complex assembly, histone dynamics, and gametophyte and sporophyte development in Arabidopsis
Erratum in
-
Correction to: The RPT2 Subunit of the 26S Proteasome Directs Complex Assembly, Histone Dynamics, and Gametophyte and Sporophyte Development in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2022 Aug 25;34(9):3482-3483. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koac170. Plant Cell. 2022. PMID: 35670749 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
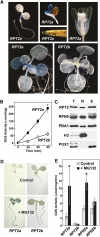
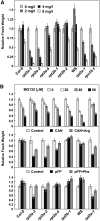
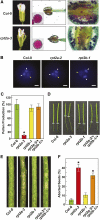
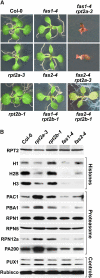
The regulatory particle (RP) of the 26S proteasome contains a heterohexameric ring of AAA-ATPases (RPT1-6) that unfolds and inserts substrates into the core protease (CP) for degradation. Through genetic analysis of the Arabidopsis thaliana gene pair encoding RPT2, we show that this subunit plays a critical role in 26S proteasome assembly, histone dynamics, and plant development. rpt2a rpt2b double null mutants are blocked in both male and female gamete transmission, demonstrating that the subunit is essential. Whereas rpt2b mutants are phenotypically normal, rpt2a mutants display a range of defects, including impaired leaf, root, trichome, and pollen development, delayed flowering, stem fasciation, hypersensitivity to mitomycin C and amino acid analogs, hyposensitivity to the proteasome inhibitor MG132, and decreased 26S complex stability. The rpt2a phenotype can be rescued by both RPT2a and RPT2b, indicative of functional redundancy, but not by RPT2a mutants altered in ATP binding/hydrolysis or missing the C-terminal hydrophobic sequence that docks the RPT ring onto the CP. Many rpt2a phenotypes are shared with mutants lacking the chromatin assembly factor complex CAF1. Like caf1 mutants, plants missing RPT2a or reduced in other RP subunits contain less histones, thus implicating RPT2 specifically, and the 26S proteasome generally, in plant nucleosome assembly.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Genetic analyses of the Arabidopsis 26S proteasome regulatory particle reveal its importance during light stress and a specific role for the N-terminus of RPT2 in development.Plant Signal Behav. 2012 Aug;7(8):973-8. doi: 10.4161/psb.20934. Epub 2012 Jul 27. Plant Signal Behav. 2012. PMID: 22836496 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis RPT2a encoding the 26S proteasome subunit is required for various aspects of root meristem maintenance, and regulates gametogenesis redundantly with its homolog, RPT2b.Plant Cell Physiol. 2011 Sep;52(9):1628-40. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcr093. Epub 2011 Jul 22. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21784786
-
A SUMO ligase AtMMS21 regulates activity of the 26S proteasome in root development.Plant Sci. 2019 Mar;280:314-320. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.12.014. Epub 2018 Dec 18. Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 30824010
-
An insight into understanding the coupling between homologous recombination mediated DNA repair and chromatin remodeling mechanisms in plant genome: an update.Cell Cycle. 2021 Sep;20(18):1760-1784. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.1966584. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Cell Cycle. 2021. PMID: 34437813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteasome regulation, plant growth and stress tolerance.Plant Signal Behav. 2009 Oct;4(10):924-7. doi: 10.4161/psb.4.10.9469. Epub 2009 Oct 29. Plant Signal Behav. 2009. PMID: 19826220 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic analyses of the Arabidopsis 26S proteasome regulatory particle reveal its importance during light stress and a specific role for the N-terminus of RPT2 in development.Plant Signal Behav. 2012 Aug;7(8):973-8. doi: 10.4161/psb.20934. Epub 2012 Jul 27. Plant Signal Behav. 2012. PMID: 22836496 Free PMC article.
-
A missense mutation of STERILE APETALA leads to female sterility in Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris ssp. pekinensis).Plant Reprod. 2019 Jun;32(2):217-228. doi: 10.1007/s00497-019-00368-7. Epub 2019 Feb 26. Plant Reprod. 2019. PMID: 30806770
-
Advanced proteomic analyses yield a deep catalog of ubiquitylation targets in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2013 May;25(5):1523-40. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.108613. Epub 2013 May 10. Plant Cell. 2013. PMID: 23667124 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of Redox Signaling in Pollen Development and Stress Response.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jan 30;11(2):287. doi: 10.3390/antiox11020287. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35204170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleolar Proteome Analysis and Proteasomal Activity Assays Reveal a Link between Nucleolus and 26S Proteasome in A. thaliana.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Oct 20;8:1815. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01815. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 29104584 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander M.P. (1969). Differential staining of aborted and nonaborted pollen. Stain Technol. 44: 117–122 - PubMed
-
- Alonso J.M., et al. (2003). Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301: 653–657 - PubMed
-
- Boisson B., Giglione C., Meinnel T. (2003). Unexpected protein families including cell defense components feature in the N-myristoylome of a higher eukaryote. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 43418–43429 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

