E74-like factor 3 (ELF3) impacts on matrix metalloproteinase 13 (MMP13) transcriptional control in articular chondrocytes under proinflammatory stress
- PMID: 22158614
- PMCID: PMC3271009
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.265744
E74-like factor 3 (ELF3) impacts on matrix metalloproteinase 13 (MMP13) transcriptional control in articular chondrocytes under proinflammatory stress
Abstract
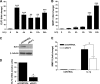
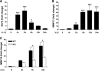
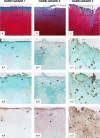
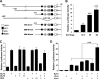
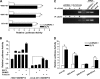
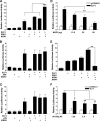
Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-13 has a pivotal, rate-limiting function in cartilage remodeling and degradation due to its specificity for cleaving type II collagen. The proximal MMP13 promoter contains evolutionarily conserved E26 transformation-specific sequence binding sites that are closely flanked by AP-1 and Runx2 binding motifs, and interplay among these and other factors has been implicated in regulation by stress and inflammatory signals. Here we report that ELF3 directly controls MMP13 promoter activity by targeting an E26 transformation-specific sequence binding site at position -78 bp and by cooperating with AP-1. In addition, ELF3 binding to the proximal MMP13 promoter is enhanced by IL-1β stimulation in chondrocytes, and the IL-1β-induced MMP13 expression is inhibited in primary human chondrocytes by siRNA-ELF3 knockdown and in chondrocytes from Elf3(-/-) mice. Further, we found that MEK/ERK signaling enhances ELF3-driven MMP13 transactivation and is required for IL-1β-induced ELF3 binding to the MMP13 promoter, as assessed by chromatin immunoprecipitation. Finally, we show that enhanced levels of ELF3 co-localize with MMP13 protein and activity in human osteoarthritic cartilage. These studies define a novel role for ELF3 as a procatabolic factor that may contribute to cartilage remodeling and degradation by regulating MMP13 gene transcription.
Figures



Similar articles
-
ELF3 modulates type II collagen gene (COL2A1) transcription in chondrocytes by inhibiting SOX9-CBP/p300-driven histone acetyltransferase activity.Connect Tissue Res. 2017 Jan;58(1):15-26. doi: 10.1080/03008207.2016.1200566. Epub 2016 Jun 16. Connect Tissue Res. 2017. PMID: 27310669 Free PMC article.
-
Regulated transcription of human matrix metalloproteinase 13 (MMP13) and interleukin-1β (IL1B) genes in chondrocytes depends on methylation of specific proximal promoter CpG sites.J Biol Chem. 2013 Apr 5;288(14):10061-10072. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.421156. Epub 2013 Feb 15. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23417678 Free PMC article.
-
Elf3 Contributes to Cartilage Degradation in vivo in a Surgical Model of Post-Traumatic Osteoarthritis.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 24;8(1):6438. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24695-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29691435 Free PMC article.
-
E74-Like Factor (ELF3) and Leptin, a Novel Loop Between Obesity and Inflammation Perpetuating a Pro-Catabolic State in Cartilage.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;45(6):2401-2410. doi: 10.1159/000488227. Epub 2018 Mar 13. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29550824
-
CDK5 Upregulated by ELF3 Transcription Promotes IL-1β-induced Inflammation and Extracellular Matrix Degradation in Human Chondrocytes.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Dec;82(4):3333-3344. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01415-5. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 39020088
Cited by
-
Overexpression of Indian hedgehog partially rescues short stature homeobox 2-overexpression-associated congenital dysplasia of the temporomandibular joint in mice.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Sep;12(3):4157-4164. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3959. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 26096903 Free PMC article.
-
ESE1 is Associated with Neuronal Apoptosis in Lipopolysaccharide Induced Neuroinflammation.Neurochem Res. 2016 Oct;41(10):2752-2762. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-1990-1. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Neurochem Res. 2016. PMID: 27350582
-
ELF3 modulates type II collagen gene (COL2A1) transcription in chondrocytes by inhibiting SOX9-CBP/p300-driven histone acetyltransferase activity.Connect Tissue Res. 2017 Jan;58(1):15-26. doi: 10.1080/03008207.2016.1200566. Epub 2016 Jun 16. Connect Tissue Res. 2017. PMID: 27310669 Free PMC article.
-
TNBC response to paclitaxel phenocopies interferon response which reveals cell cycle-associated resistance mechanisms.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 6:2024.06.04.596911. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.04.596911. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 04;15(1):4294. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82218-9. PMID: 38895265 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
TNBC response to paclitaxel phenocopies interferon response which reveals cell cycle-associated resistance mechanisms.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 4;15(1):4294. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82218-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39905117 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goldring M. B., Otero M., Plumb D. A., Dragomir C., Favero M., El Hachem K., Hashimoto K., Roach H. I., Olivotto E., Borzì R. M., Marcu K. B. (2011) Roles of inflammatory and anabolic cytokines in cartilage metabolism. Signals and multiple effectors converge upon MMP-13 regulation in osteoarthritis. Eur. Cell Mater. 21, 202–220 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Murphy G., Nagase H. (2008) Reappraising metalloproteinases in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Destruction or repair? Nat. Clin. Pract. Rheumatol. 4, 128–135 - PubMed
-
- Billinghurst R. C., Dahlberg L., Ionescu M., Reiner A., Bourne R., Rorabeck C., Mitchell P., Hambor J., Diekmann O., Tschesche H., Chen J., Van Wart H., Poole A. R. (1997) Enhanced cleavage of type II collagen by collagenases in osteoarthritic articular cartilage. J. Clin. Invest. 99, 1534–1545 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Knäuper V., López-Otin C., Smith B., Knight G., Murphy G. (1996) Biochemical characterization of human collagenase-3. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 1544–1550 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

