Whole-exome sequencing of neoplastic cysts of the pancreas reveals recurrent mutations in components of ubiquitin-dependent pathways
- PMID: 22158988
- PMCID: PMC3248495
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1118046108
Whole-exome sequencing of neoplastic cysts of the pancreas reveals recurrent mutations in components of ubiquitin-dependent pathways
Abstract
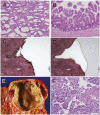
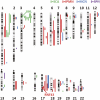
More than 2% of adults harbor a pancreatic cyst, a subset of which progresses to invasive lesions with lethal consequences. To assess the genomic landscapes of neoplastic cysts of the pancreas, we determined the exomic sequences of DNA from the neoplastic epithelium of eight surgically resected cysts of each of the major neoplastic cyst types: serous cystadenomas (SCAs), intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs), mucinous cystic neoplasms (MCNs), and solid pseudopapillary neoplasms (SPNs). SPNs are low-grade malignancies, and IPMNs and MCNs, but not SCAs, have the capacity to progress to cancer. We found that SCAs, IPMNs, MCNs, and SPNs contained 10 ± 4.6, 27 ± 12, 16 ± 7.6, and 2.9 ± 2.1 somatic mutations per tumor, respectively. Among the mutations identified, E3 ubiquitin ligase components were of particular note. Four of the eight SCAs contained mutations of the von Hippel-Lindau gene (VHL), a key component of the VHL ubiquitin ligase complex that has previously been associated with renal cell carcinomas, SCAs, and other neoplasms. Six of the eight IPMNs and three of the eight MCNs harbored mutations of RNF43, a gene coding for a protein with intrinsic E3 ubiquitin ligase activity that has not previously been found to be genetically altered in any human cancer. The preponderance of inactivating mutations in RNF43 unequivocally establish it as a suppressor of both IPMNs and MCNs. SPNs contained remarkably few genetic alterations but always contained mutations of CTNNB1, previously demonstrated to inhibit degradation of the encoded protein (β-catenin) by E3 ubiquitin ligases. These results highlight the essential role of ubiquitin ligases in these neoplasms and have important implications for the diagnosis and treatment of patients with cystic tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Garcea G, et al. Cystic lesions of the pancreas. A diagnostic and management dilemma. Pancreatology. 2008;8:236–251. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka M. Controversies in the management of pancreatic IPMN. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;8:56–60. - PubMed
-
- Kimura W, Nagai H, Kuroda A, Muto T, Esaki Y. Analysis of small cystic lesions of the pancreas. Int J Pancreatol. 1995;18:197–206. - PubMed
-
- Zhang XM, Mitchell DG, Dohke M, Holland GA, Parker L. Pancreatic cysts: Depiction on single-shot fast spin-echo MR images. Radiology. 2002;223:547–553. - PubMed
-
- de Jong K, et al. High prevalence of pancreatic cysts detected by screening magnetic resonance imaging examinations. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;8:806–811. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01-CN-43302/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA062924/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN043309/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- P01 CA134292/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 43460/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA152432/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA057345/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA057345/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 152432/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN043302/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01CA134292/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 57345/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA043460/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 62924/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CN-43309/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

