Cell organization, growth, and neural and cardiac development require αII-spectrin
- PMID: 22159418
- PMCID: PMC3244980
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.080374
Cell organization, growth, and neural and cardiac development require αII-spectrin
Abstract
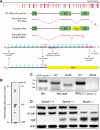
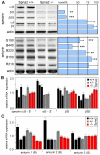
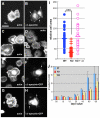
Spectrin α2 (αII-spectrin) is a scaffolding protein encoded by the Spna2 gene and constitutively expressed in most tissues. Exon trapping of Spna2 in C57BL/6 mice allowed targeted disruption of αII-spectrin. Heterozygous animals displayed no phenotype by 2 years of age. Homozygous deletion of Spna2 was embryonic lethal at embryonic day 12.5 to 16.5 with retarded intrauterine growth, and craniofacial, neural tube and cardiac anomalies. The loss of αII-spectrin did not alter the levels of αI- or βI-spectrin, or the transcriptional levels of any β-spectrin or any ankyrin, but secondarily reduced by about 80% the steady state protein levels of βII- and βIII-spectrin. Residual βII- and βIII-spectrin and ankyrins B and G were concentrated at the apical membrane of bronchial and renal epithelial cells, without impacting cell morphology. Neuroepithelial cells in the developing brain were more concentrated and more proliferative in the ventricular zone than normal; axon formation was also impaired. Embryonic fibroblasts cultured on fibronectin from E14.5 (Spna2(-/-)) animals displayed impaired growth and spreading, a spiky morphology, and sparse lamellipodia without cortical actin. These data indicate that the spectrin-ankyrin scaffold is crucial in vertebrates for cell spreading, tissue patterning and organ development, particularly in the developing brain and heart, but is not required for cell viability.
Figures



Similar articles
-
An αII Spectrin-Based Cytoskeleton Protects Large-Diameter Myelinated Axons from Degeneration.J Neurosci. 2017 Nov 22;37(47):11323-11334. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2113-17.2017. Epub 2017 Oct 16. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29038243 Free PMC article.
-
AlphaII-spectrin participates in the surface expression of cell adhesion molecule L1 and neurite outgrowth.Exp Cell Res. 2014 Apr 1;322(2):365-80. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.01.012. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Exp Cell Res. 2014. PMID: 24462599
-
Dysfunction in the βII spectrin-dependent cytoskeleton underlies human arrhythmia.Circulation. 2015 Feb 24;131(8):695-708. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.013708. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Circulation. 2015. PMID: 25632041 Free PMC article.
-
An Adaptable Spectrin/Ankyrin-Based Mechanism for Long-Range Organization of Plasma Membranes in Vertebrate Tissues.Curr Top Membr. 2016;77:143-84. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctm.2015.10.001. Epub 2015 Nov 30. Curr Top Membr. 2016. PMID: 26781832 Review.
-
Evolution of spectrin function in cytoskeletal and membrane networks.Biochem Soc Trans. 2009 Aug;37(Pt 4):796-803. doi: 10.1042/BST0370796. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009. PMID: 19614597 Review.
Cited by
-
The spectrin cytoskeleton integrates endothelial mechanoresponses.Nat Cell Biol. 2022 Aug;24(8):1226-1238. doi: 10.1038/s41556-022-00953-5. Epub 2022 Jul 11. Nat Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35817960
-
Supporting the heart: Functions of the cardiomyocyte's non-sarcomeric cytoskeleton.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2019 Jun;131:187-196. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2019.04.002. Epub 2019 Apr 9. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30978342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinformatic identification of key candidate genes and pathways in axon regeneration after spinal cord injury in zebrafish.Neural Regen Res. 2020 Jan;15(1):103-111. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.264460. Neural Regen Res. 2020. PMID: 31535658 Free PMC article.
-
Pilot study evaluating everolimus molecular mechanisms in tuberous sclerosis complex and focal cortical dysplasia.PLoS One. 2022 May 19;17(5):e0268597. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0268597. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35587487 Free PMC article.
-
An αII Spectrin-Based Cytoskeleton Protects Large-Diameter Myelinated Axons from Degeneration.J Neurosci. 2017 Nov 22;37(47):11323-11334. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2113-17.2017. Epub 2017 Oct 16. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29038243 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bennett V., Baines A. J. (2001). Spectrin and ankyrin-based pathways: metazoan inventions for integrating cells into tissues. Physiol. Rev. 81, 1353-1392 - PubMed
-
- Bennett V., Healy J. (2008). Organizing the fluid membrane bilayer: diseases linked to spectrin and ankyrin. Trends Mol. Med. 14, 28-36 - PubMed
-
- Bialkowska K., Saido T. C., Fox J. E. (2005). SH3 domain of spectrin participates in the activation of Rac in specialized calpain-induced integrin signaling complexes. J. Cell Sci. 118, 381-395 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

