WRN helicase regulates the ATR-CHK1-induced S-phase checkpoint pathway in response to topoisomerase-I-DNA covalent complexes
- PMID: 22159421
- PMCID: PMC3244981
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.081372
WRN helicase regulates the ATR-CHK1-induced S-phase checkpoint pathway in response to topoisomerase-I-DNA covalent complexes
Abstract
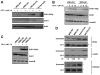
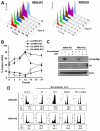
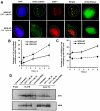
Checkpoints are cellular surveillance and signaling pathways that coordinate the response to DNA damage and replicative stress. Consequently, failure of cellular checkpoints increases susceptibility to DNA damage and can lead to profound genome instability. This study examines the role of a human RECQ helicase, WRN, in checkpoint activation in response to DNA damage. Mutations in WRN lead to genomic instability and the premature aging condition Werner syndrome. Here, the role of WRN in a DNA-damage-induced checkpoint was analyzed in U-2 OS (WRN wild type) and isogenic cells stably expressing WRN-targeted shRNA (WRN knockdown). The results of our studies suggest that WRN has a crucial role in inducing an S-phase checkpoint in cells exposed to the topoisomerase I inhibitor campthothecin (CPT), but not in cells exposed to hydroxyurea. Intriguingly, WRN decreases the rate of replication fork elongation, increases the accumulation of ssDNA and stimulates phosphorylation of CHK1, which releases CHK1 from chromatin in CPT-treated cells. Importantly, knockdown of WRN expression abolished or delayed all these processes in response to CPT. Together, our results strongly suggest an essential regulatory role for WRN in controlling the ATR-CHK1-mediated S-phase checkpoint in CPT-treated cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Checkpoint-dependent and independent roles of the Werner syndrome protein in preserving genome integrity in response to mild replication stress.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Nov 10;42(20):12628-39. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1022. Epub 2014 Oct 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25352544 Free PMC article.
-
The Werner syndrome protein: linking the replication checkpoint response to genome stability.Aging (Albany NY). 2011 Mar;3(3):311-8. doi: 10.18632/aging.100293. Aging (Albany NY). 2011. PMID: 21389352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The RAD9-RAD1-HUS1 (9.1.1) complex interacts with WRN and is crucial to regulate its response to replication fork stalling.Oncogene. 2012 Jun 7;31(23):2809-23. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.468. Epub 2011 Oct 17. Oncogene. 2012. PMID: 22002307 Free PMC article.
-
WRN is required for ATM activation and the S-phase checkpoint in response to interstrand cross-link-induced DNA double-strand breaks.Mol Biol Cell. 2008 Sep;19(9):3923-33. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-07-0698. Epub 2008 Jul 2. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18596239 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between wrn and the checkpoint in s-phase.Ital J Biochem. 2007 Jun;56(2):130-40. Ital J Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17722654 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of Origin, Phenotypic Effects and Diagnostic Implications of Complex Chromosome Rearrangements.Mol Syndromol. 2015 Sep;6(3):110-34. doi: 10.1159/000438812. Epub 2015 Aug 15. Mol Syndromol. 2015. PMID: 26732513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RECQL5 plays co-operative and complementary roles with WRN syndrome helicase.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jan;41(2):881-99. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1134. Epub 2012 Nov 23. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23180761 Free PMC article.
-
RecQ DNA Helicase Rqh1 Promotes Rad3ATR Kinase Signaling in the DNA Replication Checkpoint Pathway of Fission Yeast.Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Aug 14;40(17):e00145-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00145-20. Print 2020 Aug 14. Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32541066 Free PMC article.
-
Checkpoint functions of RecQ helicases at perturbed DNA replication fork.Curr Genet. 2021 Jun;67(3):369-382. doi: 10.1007/s00294-020-01147-y. Epub 2021 Jan 11. Curr Genet. 2021. PMID: 33427950 Review.
-
Human RecQ helicases in DNA repair, recombination, and replication.Annu Rev Biochem. 2014;83:519-52. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060713-035428. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Annu Rev Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24606147 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baynton K., Otterlei M., Bjørås M., Kobbe C., Bohr V. A., Seeberg E. (2003). WRN interacts physically and functionally with the recombination mediator protein RAD52. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 36476-36486 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

