Activation-induced cell death of memory CD8+ T cells from pleural effusion of lung cancer patients is mediated by the type II Fas-induced apoptotic pathway
- PMID: 22159518
- PMCID: PMC11028981
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-011-1165-5
Activation-induced cell death of memory CD8+ T cells from pleural effusion of lung cancer patients is mediated by the type II Fas-induced apoptotic pathway
Abstract
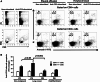
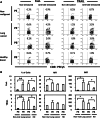
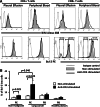
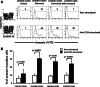
Lung cancer is the second most common form of cancer and the leading cause of cancer death worldwide. Pleural effusions, containing high numbers of mononuclear and tumor cells, are frequent in patients with advanced stages of lung cancer. We reported that in pleural effusions from primary lung cancer, the CD8+ T cell subpopulation, and particularly the terminally differentiated subset, is reduced compared to that of non-malignant effusions. We analyzed the participation of activation-induced cell death (AICD) and extrinsic pathways (type I or II) as mechanisms for the decrease in pleural effusion CD8+ T cell subpopulation. Pleural effusion or peripheral blood CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, from lung cancer patients, were stimulated with anti-CD3 antibody and analyzed for (a) apoptosis by annexin-V-binding and TUNEL assay, (b) transcript levels of Fas ligand (FasL) and TRAIL by real-time RT-PCR, (c) expression of FasL and TRAIL, measured as integrated mean fluorescence intensities (iMFI) by flow cytometry, (d) expression of Bcl-2 and BIM molecules, measured as MFI, and (e) apoptosis inhibition using caspase-8 and -9 inhibitors. Pleural effusion CD8+ T cells, but not CD4+ T cells, from cancer patients underwent AICD. Blocking FasL/Fas pathway protected from AICD. Upregulation of FasL and TRAIL expressions was found in pleural effusion CD8+ T cells, which also showed a subset of Bcl-2 low cells. In memory CD8+ T cells, AICD depended on both extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways. Hence, in the pleural space of lung cancer patients, AICD might compromise the antitumor function of CD8+ T cells.
Figures




References
-
- Pace E, Bruno TF, Berenger B, Mody CH, Melis M, Ferraro M, Tipa A, Bruno A, Profita M, Bonsignore G, Gjomarkaj M. Elevated expression of prostaglandin receptor and increased release of prostaglandin E2 maintain the survival of CD45RO+ T cells in the inflamed human pleural space. Immunology. 2007;121:427–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02593.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

