Triplatin, a platelet aggregation inhibitor from the salivary gland of the triatomine vector of Chagas disease, binds to TXA(2) but does not interact with glycoprotein PVI
- PMID: 22159626
- PMCID: PMC3408606
- DOI: 10.1160/TH11-10-0685
Triplatin, a platelet aggregation inhibitor from the salivary gland of the triatomine vector of Chagas disease, binds to TXA(2) but does not interact with glycoprotein PVI
Abstract
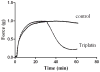
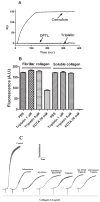
Salivary glands from haematophagous animals express a notable diversity of negative modulators of platelet function. Triplatin is an inhibitor of collagen-induced platelet aggregation which has been described as an antagonist of glycoprotein VI (GPVI). Because triplatin displays sequence homology to members of the lipocalin family of proteins, we investigated whether triplatin mechanism of action could be explained by interaction with pro-haemostatic prostaglandins. Our results demonstrate that triplatin inhibits platelet aggregation induced by low doses of collagen, thromboxane A2 (TXA(2)) mimetic (U46619), and arachidonic acid (AA). On the other hand, it does not inhibit platelet aggregation by convulxin, PMA, or low-dose ADP. Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) revealed that triplatin binds AA, cTXA(2), TXB(2), U46619 or prostaglandin (PG)H(2) mimetic (U51605). Consistent with its ligand specificity, triplatin induces relaxation of rat aorta contracted with U46619. Triplatin also interacts with PGF(2α) and PGJ(2), but not with leukotrienes, AA or biogenic amines. Surface plasmon resonance experiments failed to demonstrate interaction of triplatin with GPVI; it also did to inhibit platelet adhesion to fibrillar or soluble collagen. Because triplatin displays sequence similarity to apolipoprotein D (ApoD) - a lipocalin associated with high-density lipoprotein, ApoD was tested as a putative TXA(2)-binding molecule. ITC failed to demonstrate binding of ApoD to all prostanoids described above, or to AA. Furthermore, ApoD was devoid of inhibitory properties towards platelets activation by AA, collagen, or U46619. In conclusion, triplatin mechanism of action has been elucidated without ambiguity as a novel TXA(2)- and PGF(2α)- binding protein. It conceivably blocks platelet aggregation and vasoconstriction, thus contributing to successful blood feeding at the vector-host interface.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they do not have direct or indirect conflicts of interest such as relationships with industry through investments, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or honoraria.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Dipetalodipin, a novel multifunctional salivary lipocalin that inhibits platelet aggregation, vasoconstriction, and angiogenesis through unique binding specificity for TXA2, PGF2alpha, and 15(S)-HETE.J Biol Chem. 2010 Dec 10;285(50):39001-12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.152835. Epub 2010 Oct 2. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20889972 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of a collagen-induced platelet aggregation inhibitor, triplatin, from salivary glands of the assassin bug, Triatoma infestans.FEBS J. 2006 Jul;273(13):2955-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2006.05306.x. Epub 2006 Jun 6. FEBS J. 2006. PMID: 16759235
-
Novel angiotensin II AT(1) receptor antagonist irbesartan prevents thromboxane A(2)-induced vasoconstriction in canine coronary arteries and human platelet aggregation.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000 Jan;292(1):238-46. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000. PMID: 10604953
-
Salivary Thromboxane A2-Binding Proteins from Triatomine Vectors of Chagas Disease Inhibit Platelet-Mediated Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) Formation and Arterial Thrombosis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015 Jun 25;9(6):e0003869. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003869. eCollection 2015. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015. PMID: 26110417 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet aggregation inhibitors from hematophagous animals.Toxicon. 2010 Dec 15;56(7):1130-44. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2009.12.003. Epub 2009 Dec 24. Toxicon. 2010. PMID: 20035779 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the molecular complexity of Triatoma dimidiata sialome.J Proteomics. 2018 Mar 1;174:47-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2017.12.016. Epub 2017 Dec 27. J Proteomics. 2018. PMID: 29288089 Free PMC article.
-
An insight into the salivary gland and fat body transcriptome of Panstrongylus lignarius (Hemiptera: Heteroptera), the main vector of Chagas disease in Peru.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018 Feb 20;12(2):e0006243. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006243. eCollection 2018 Feb. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018. PMID: 29462134 Free PMC article.
-
An Insight into the Triabin Protein Family of American Hematophagous Reduviids: Functional, Structural and Phylogenetic Analysis.Toxins (Basel). 2016 Feb 15;8(2):44. doi: 10.3390/toxins8020044. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 26891325 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-complement activity in salivary glands and midgut of Chagas disease vector, Panstrongylus megistus (Hemiptera, Triatominae).Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2019 Aug 8;61:e38. doi: 10.1590/S1678-9946201961038. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2019. PMID: 31411268 Free PMC article.
-
Lufaxin, a novel factor Xa inhibitor from the salivary gland of the sand fly Lutzomyia longipalpis blocks protease-activated receptor 2 activation and inhibits inflammation and thrombosis in vivo.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012 Sep;32(9):2185-98. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.253906. Epub 2012 Jul 12. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012. PMID: 22796577 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Watson SP. Platelet activation by extracellular matrix proteins in haemostasis and thrombosis. Curr Pharm Des. 2009;15(12):1358–72. - PubMed
-
- Nieswandt B, Watson SP. Platelet-collagen interaction: is GPVI the central receptor? Blood. 2003 Jul 15;102(2):449–61. - PubMed
-
- Jung SM, Moroi M. Activation of the platelet collagen receptor integrin alpha(2)beta(1): its mechanism and participation in the physiological functions of platelets. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2000 Oct;10(7):285–92. - PubMed
-
- Cosemans JM, Iserbyt BF, Deckmyn H, et al. Multiple ways to switch platelet integrins on and off. J Thromb Haemost. 2008 Aug;6(8):1253–61. - PubMed
-
- Gibbins JM. Platelet adhesion signalling and the regulation of thrombus formation. J Cell Sci. 2004 Jul 15;117(Pt 16):3415–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

