Median preoptic nucleus and subfornical organ drive renal sympathetic nerve activity via a glutamatergic mechanism within the paraventricular nucleus
- PMID: 22160544
- PMCID: PMC3293509
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00403.2011
Median preoptic nucleus and subfornical organ drive renal sympathetic nerve activity via a glutamatergic mechanism within the paraventricular nucleus
Abstract
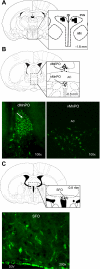
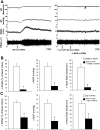
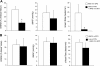
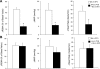
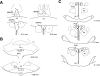
The paraventricular nucleus (PVN) of the hypothalamus is involved in the neural control of sympathetic drive, but the precise mechanism(s) that influences the PVN is not known. The activation of the PVN may be influenced by input from higher forebrain areas, such as the median preoptic nucleus (MnPO) and the subfornical organ (SFO). We hypothesized that activation of the MnPO or SFO would drive the PVN through a glutamatergic pathway. Neuroanatomical connections were confirmed by the recovery of a retrograde tracer in the MnPO and SFO that was injected bilaterally into the PVN in rats. Microinjection of 200 pmol of N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) or bicuculline-induced activation of the MnPO and increased renal sympathetic activity (RSNA), mean arterial pressure, and heart rate in anesthetized rats. These responses were attenuated by prior microinjection of a glutamate receptor blocker AP5 (4 nmol) into the PVN (NMDA - ΔRSNA 72 ± 8% vs. 5 ± 1%; P < 0.05). Using single-unit extracellular recording, we examined the effect of NMDA microinjection (200 pmol) into the MnPO on the firing activity of PVN neurons. Of the 11 active neurons in the PVN, 6 neurons were excited by 95 ± 17% (P < 0.05), 1 was inhibited by 57%, and 4 did not respond. The increased RSNA after activation of the SFO by ANG II (1 nmol) or bicuculline (200 pmol) was also reduced by AP5 in the PVN (for ANG II - ΔRSNA 46 ± 7% vs. 17 ± 4%; P < 0.05). Prior microinjection of ANG II type 1 receptor blocker losartan (4 nmol) into the PVN did not change the response to ANG II or bicuculline microinjection into the SFO. The results from this study demonstrate that the sympathoexcitation mediated by a glutamatergic mechanism in the PVN is partially driven by the activation of the MnPO or SFO.
Figures
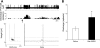
Similar articles
-
Interaction between glutamate and GABA systems in the integration of sympathetic outflow by the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006 Dec;291(6):H2847-56. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00625.2005. Epub 2006 Jul 28. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16877560
-
Subfornical organ and hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus connections with median preoptic nucleus neurons: an electrophysiological study in the rat.Exp Brain Res. 1987;68(3):579-85. doi: 10.1007/BF00249800. Exp Brain Res. 1987. PMID: 3691728
-
Sympathoexcitation by PVN-injected bicuculline requires activation of excitatory amino acid receptors.Hypertension. 2003 Oct;42(4):725-31. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000085197.20043.44. Epub 2003 Aug 4. Hypertension. 2003. PMID: 12900439
-
The paraventricular nucleus: an important component of the central neurocircuitry regulating sympathetic nerve outflow.Acta Physiol Scand. 2003 Jan;177(1):7-15. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-201X.2003.01042.x. Acta Physiol Scand. 2003. PMID: 12492774 Review.
-
Preoptic–Periventricular Integrative Mechanisms Involved in Behavior, Fluid–Electrolyte Balance, and Pressor Responses.In: De Luca LA Jr, Menani JV, Johnson AK, editors. Neurobiology of Body Fluid Homeostasis: Transduction and Integration. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2014. Chapter 4. In: De Luca LA Jr, Menani JV, Johnson AK, editors. Neurobiology of Body Fluid Homeostasis: Transduction and Integration. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2014. Chapter 4. PMID: 24829988 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Central Angiotensin-II Increases Blood Pressure and Sympathetic Outflow via Rho Kinase Activation in Conscious Rabbits.Hypertension. 2016 Nov;68(5):1271-1280. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.07792. Epub 2016 Sep 26. Hypertension. 2016. PMID: 27672026 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II, Oxidative Stress, and Sympathetic Nervous System Hyperactivity in Heart Failure.Yonago Acta Med. 2018 Jun 18;61(2):103-109. doi: 10.33160/yam.2018.06.002. eCollection 2018 Jun. Yonago Acta Med. 2018. PMID: 29946216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin II Type 1a Receptors in the Subfornical Organ Modulate Neuroinflammation in the Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus in Heart Failure Rats.Neuroscience. 2018 Jun 15;381:46-58. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.04.012. Epub 2018 Apr 21. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 29684507 Free PMC article.
-
AT1a-dependent GABAA inhibition in the MnPO following chronic intermittent hypoxia.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2021 Sep 1;321(3):R469-R481. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00030.2021. Epub 2021 Jun 30. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34189959 Free PMC article.
-
RCAN1-Mediated Calcineurin Impairment Drives Sympathetic Outflow in Hypertension.Circ Res. 2025 Jul 18;137(3):417-434. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.124.325975. Epub 2025 Jun 13. Circ Res. 2025. PMID: 40510021
References
-
- Badoer E. Hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus and cardiovascular regulation. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 28: 95–99, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Badoer E. Neurons in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus that project to the rostral ventrolateral medulla are not activated by hypotension. Brain Res 801: 224–227, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Bains JS, Ferguson AV. Paraventricular nucleus neurons projecting to the spinal cord receive excitatory input from the subfornical organ. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 268: R625–R633, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Chen QH, Haywood JR, Toney GM. Sympathoexcitation by PVN-injected bicuculline requires activation of excitatory amino acid receptors. Hypertension 42: 725–731, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Chen QH, Toney GM. Responses to GABA-A receptor blockade in the hypothalamic PVN are attenuated by local AT1 receptor antagonism. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 285: R1231–R1239, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

