Promiscuous targeting of polytopic membrane proteins to SecYEG or YidC by the Escherichia coli signal recognition particle
- PMID: 22160593
- PMCID: PMC3268725
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E11-07-0590
Promiscuous targeting of polytopic membrane proteins to SecYEG or YidC by the Escherichia coli signal recognition particle
Abstract
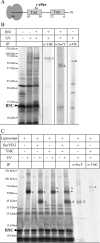
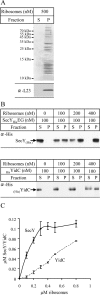
Protein insertion into the bacterial inner membrane is facilitated by SecYEG or YidC. Although SecYEG most likely constitutes the major integration site, small membrane proteins have been shown to integrate via YidC. We show that YidC can also integrate multispanning membrane proteins such as mannitol permease or TatC, which had been considered to be exclusively integrated by SecYEG. Only SecA-dependent multispanning membrane proteins strictly require SecYEG for integration, which suggests that SecA can only interact with the SecYEG translocon, but not with the YidC insertase. Targeting of multispanning membrane proteins to YidC is mediated by signal recognition particle (SRP), and we show by site-directed cross-linking that the C-terminus of YidC is in contact with SRP, the SRP receptor, and ribosomal proteins. These findings indicate that SRP recognizes membrane proteins independent of the downstream integration site and that many membrane proteins can probably use either SecYEG or YidC for integration. Because protein synthesis is much slower than protein transport, the use of YidC as an additional integration site for multispanning membrane proteins may prevent a situation in which the majority of SecYEG complexes are occupied by translating ribosomes during cotranslational insertion, impeding the translocation of secretory proteins.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The interaction network of the YidC insertase with the SecYEG translocon, SRP and the SRP receptor FtsY.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 12;8(1):578. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-19019-w. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29330529 Free PMC article.
-
Both YidC and SecYEG are required for translocation of the periplasmic loops 1 and 2 of the multispanning membrane protein TatC.J Mol Biol. 2012 Dec 14;424(5):354-67. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.09.026. Epub 2012 Oct 8. J Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 23058713
-
The integration of YidC into the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli requires the signal recognition particle, SecA and SecYEG.J Biol Chem. 2002 Feb 22;277(8):5715-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C100683200. Epub 2002 Jan 3. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11777926
-
YidC as a potential antibiotic target.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2023 Feb;1870(2):119403. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2022.119403. Epub 2022 Nov 23. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2023. PMID: 36427551 Review.
-
The ribosome and YidC. New insights into the biogenesis of Escherichia coli inner membrane proteins.EMBO Rep. 2003 Oct;4(10):939-43. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.embor921. EMBO Rep. 2003. PMID: 14528263 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An alternative pathway for membrane protein biogenesis at the endoplasmic reticulum.Commun Biol. 2021 Jul 1;4(1):828. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02363-z. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 34211117 Free PMC article.
-
Insertion and folding pathways of single membrane proteins guided by translocases and insertases.Sci Adv. 2019 Jan 30;5(1):eaau6824. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aau6824. eCollection 2019 Jan. Sci Adv. 2019. PMID: 30801000 Free PMC article.
-
Cotranslational Biogenesis of Membrane Proteins in Bacteria.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Apr 29;9:871121. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.871121. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35573737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid dependencies, biogenesis and cytoplasmic micellar forms of integral membrane sugar transport proteins of the bacterial phosphotransferase system.Microbiology (Reading). 2013 Nov;159(Pt 11):2213-2224. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.070953-0. Epub 2013 Aug 28. Microbiology (Reading). 2013. PMID: 23985145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interaction network of the YidC insertase with the SecYEG translocon, SRP and the SRP receptor FtsY.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 12;8(1):578. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-19019-w. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29330529 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beha D, Deitermann S, Muller M, Koch HG. Export of beta-lactamase is independent of the signal recognition particle. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:22161–22167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

