Structural interconversions modulate activity of Escherichia coli ribonucleotide reductase
- PMID: 22160671
- PMCID: PMC3248520
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1112715108
Structural interconversions modulate activity of Escherichia coli ribonucleotide reductase
Abstract
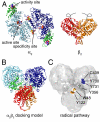
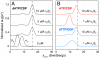
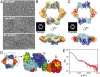
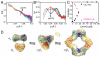
Essential for DNA biosynthesis and repair, ribonucleotide reductases (RNRs) convert ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides via radical-based chemistry. Although long known that allosteric regulation of RNR activity is vital for cell health, the molecular basis of this regulation has been enigmatic, largely due to a lack of structural information about how the catalytic subunit (α(2)) and the radical-generation subunit (β(2)) interact. Here we present the first structure of a complex between α(2) and β(2) subunits for the prototypic RNR from Escherichia coli. Using four techniques (small-angle X-ray scattering, X-ray crystallography, electron microscopy, and analytical ultracentrifugation), we describe an unprecedented α(4)β(4) ring-like structure in the presence of the negative activity effector dATP and provide structural support for an active α(2)β(2) configuration. We demonstrate that, under physiological conditions, E. coli RNR exists as a mixture of transient α(2)β(2) and α(4)β(4) species whose distributions are modulated by allosteric effectors. We further show that this interconversion between α(2)β(2) and α(4)β(4) entails dramatic subunit rearrangements, providing a stunning molecular explanation for the allosteric regulation of RNR activity in E. coli.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Licht S, Gerfen GJ, Stubbe J. Thiyl radicals in ribonucleotide reductases. Science. 1996;271:477–481. - PubMed
-
- Jordan A, Reichard P. Ribonucleotide reductases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:71–98. - PubMed
-
- Nordlund P, Reichard P. Ribonucleotide reductases. Annu Rev Biochem. 2006;75:681–706. - PubMed
-
- Brown NC, Reichard P. Role of effector binding in allosteric control of ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase. J Mol Biol. 1969;46:39–55. - PubMed
-
- Eriksson M, et al. Binding of allosteric effectors to ribonucleotide reductase protein R1: Reduction of active-site cysteines promotes substrate binding. Structure. 1997;5:1077–1092. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- F32 DK080622/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM067167/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008334/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM29595/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RR-01646/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM08334/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM029595/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- P41 RR017573/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- F32DK080622/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR001646/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- GM67167/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32GM904862/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

