Macrophages participate in IL-17-mediated inflammation
- PMID: 22161142
- PMCID: PMC4292791
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.201141737
Macrophages participate in IL-17-mediated inflammation
Abstract
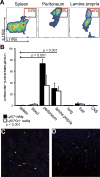
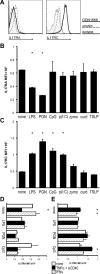
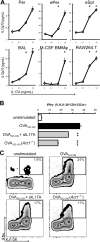
The involvement of macrophages (MΦs) in Th17-cell responses is still poorly understood. While neutrophils are thought to be the predominant effector of Th17-cell responses, IL-17 is also known to induce myelotropic chemokines and growth factors. Other T-cell-derived cytokines induce non-classical functions, suggesting that IL-17 sigxnaling may similarly elicit unique MΦ functions. Here, we characterized the expression of subunits of the IL-17 receptor on primary murine MΦs from different anatomical compartments. The greatest expression of IL-17 receptors was observed on mucosal Ly6C(hi) "inflammatory" MΦs. We further observed upregulation of IL-17 receptors in vitro on bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMMΦs) in response to peptidoglycan or CpG oligonucleotide stimuli, and in vivo, upon CFA administration. Macrophages expressing IL-17 receptors were observed infiltrating the hearts of mice with myocarditis, and genetic ablation of IL-17RA altered MΦ recruitment. Treating primary MΦs from a wide variety of different anatomic sources (as well as cell lines) with IL-17A induced the production of unique profiles of cytokines and chemokines, including GM-CSF, IL-3, IL-9, CCL4/MIP-1β and CCL5/RANTES. IL-17A also induced production of IL-12p70; IL-17-signaling-deficient MΦs elicited diminished IFN-γ production by responding DO11.10 CD4(+) T cells when used as APCs. These data indicate that MΦs from different anatomic locations direct IL-17-mediated responses.
Copyright © 2012 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Involvement of mannose receptor in cytokine interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta), IL-6, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor responses, but not in chemokine macrophage inflammatory protein 1beta (MIP-1beta), MIP-2, and KC responses, caused by attachment of Candida albicans to macrophages.Infect Immun. 1997 Mar;65(3):1077-82. doi: 10.1128/IAI.65.3.1077-1082.1997. Infect Immun. 1997. PMID: 9038318 Free PMC article.
-
CSF-1-dependent red pulp macrophages regulate CD4 T cell responses.J Immunol. 2011 Feb 15;186(4):2229-37. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1001345. Epub 2011 Jan 14. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21239712
-
Unique macrophages different from M1/M2 macrophages inhibit T cell mitogenesis while upregulating Th17 polarization.Sci Rep. 2014 Feb 20;4:4146. doi: 10.1038/srep04146. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24553452 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-17 family cytokines in protective immunity against infections: role of hematopoietic cell-derived and non-hematopoietic cell-derived interleukin-17s.Microbiol Immunol. 2018 Jan;62(1):1-13. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12560. Microbiol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29205464 Review.
-
Macrophages make me sick: how macrophage activation states influence sickness behavior.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2011 Nov;36(10):1431-40. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2011.07.002. Epub 2011 Aug 19. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2011. PMID: 21855222 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Natural killer cells limit cardiac inflammation and fibrosis by halting eosinophil infiltration.Am J Pathol. 2015 Mar;185(3):847-61. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2014.11.023. Epub 2015 Jan 23. Am J Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25622543 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual dimorphic function of IL-17 in salivary gland dysfunction of the C57BL/6.NOD-Aec1Aec2 model of Sjögren's syndrome.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 13;6:38717. doi: 10.1038/srep38717. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27958291 Free PMC article.
-
Streptococcus gallolyticus supernatant induces M2 macrophage polarization and activates IL-17 F signaling in colorectal tumorigenesis.Gut Pathog. 2025 Aug 12;17(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s13099-025-00731-2. Gut Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40797334 Free PMC article.
-
IL-21R signaling suppresses IL-17+ gamma delta T cell responses and production of IL-17 related cytokines in the lung at steady state and after Influenza A virus infection.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 7;10(4):e0120169. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120169. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25849970 Free PMC article.
-
Coxiella burnetii Blocks Intracellular Interleukin-17 Signaling in Macrophages.Infect Immun. 2018 Sep 21;86(10):e00532-18. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00532-18. Print 2018 Oct. Infect Immun. 2018. PMID: 30061378 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Veldhoen M, Hocking RJ, Atkins CJ, Locksley RM, Stockinger B. TGFbeta in the context of an inflammatory cytokine milieu supports de novo differentiation of IL-17-producing T cells. Immunity. 2006;24:179–189. - PubMed
-
- Harrington LE, Hatton RD, Mangan PR, Turner H, Murphy TL, Murphy KM, Weaver CT. Interleukin 17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nature immunology. 2005;6:1123–1132. - PubMed
-
- Weaver CT, Harrington LE, Mangan PR, Gavrieli M, Murphy KM. Th17: an effector CD4 T cell lineage with regulatory T cell ties. Immunity. 2006;24:677–688. - PubMed
-
- Korn T, Bettelli E, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK. IL-17 and Th17 Cells. Annual Review of Immunology. 2009;27:485–517. - PubMed
-
- Kolls JK, Linden A. Interleukin-17 family members and inflammation. Immunity. 2004;21:467–476. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

