Botulinum toxin injections for adults with overactive bladder syndrome
- PMID: 22161392
- PMCID: PMC12527225
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005493.pub3
Botulinum toxin injections for adults with overactive bladder syndrome
Abstract
Background: Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) is a common condition with a significant negative impact on quality of life characterised by urgency with or without urge incontinence, frequency and nocturia. Intravesical botulinum toxin is being increasingly used to treat severe overactive bladder refractory to standard management. An increasing body of literature is forming that supports this technique as effective, well tolerated, and safe. This review is a substantial update of the 2007 review of the same title.
Objectives: The objective was to compare intravesical botulinum toxin with other treatments for neurogenic and idiopathic overactive bladder in adults. The hypothesis to be addressed were whether intravesical injection of botulinum toxin was better than placebo or no treatment; pharmacological and other non-pharmacological interventions; whether higher doses of botulinum toxin were better than lower doses; whether botulinum toxin in combination with other treatments was better than other treatments alone; whether one formulation of botulinum toxin is better than another; and whether one injection technique was better than another.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Incontinence Group Specialised Trials Register (searched 23 February 2010). The Register contains trials identified from MEDLINE, CINAHL, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), and handsearching of journals and conference proceedings. Additionally, all reference lists of selected trials and relevant review papers were searched. No limitations were placed on the searches.
Selection criteria: All randomised or quasi-randomised controlled trials of treatment for OAB in adults in which at least one management arm involved intravesical injection of botulinum toxin were included. Participants had either neurogenic OAB or idiopathic OAB with or without stress incontinence. Comparison interventions could include no intervention, placebo, lifestyle modification, bladder retraining, pharmacological treatments, surgery, bladder instillation techniques, neuromodulation, and different types, doses, and injection techniques of botulinum toxin.
Data collection and analysis: Binary outcomes were presented as relative risk and continuous outcomes by mean differences. Little data could be synthesised across studies due to differing study designs and outcome measures. Where applicable standard deviations were calculated from P values according to the formula described in section 7.7.3.3 of the Cochrane Handbook of Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Data were tabulated where possible with results taken from trial reports where this was not possible. Where multiple publications were found, the reports were treated as a single source of data.
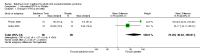
Main results: Nineteen studies were identified that met the inclusion criteria. Most patients in the studies had neurogenic OAB, but some included patients with idiopathic OAB. All studies demonstrated superiority of botulinum toxin to placebo. Lower doses of botulinum toxin (100 to 150 U) appeared to have beneficial effects, but larger doses (300 U) may have been more effective and longer lasting, but with more side effects. Suburothelial injection had comparable efficacy to intradetrusor injection. The effect of botulinum toxin may last for a number of months and is dependent upon dose and type of toxin used. Patients receiving repeated doses do not seem to become refractory to botulinum toxin. Botulinum toxin appeared to have beneficial effects in OAB that quantitatively exceeded the effects of intravesical resiniferatoxin. Intravesical botulinum toxin appeared to be reasonably safe; however, one study was halted due to a perceived unacceptable rate of urinary retention.
Authors' conclusions: Intravesical botulinum toxin appears to be an effective therapy for refractory OAB symptoms, but as yet little controlled trial data exist on benefits and safety compared with other interventions, or with placebo. Further robust data are required on long term outcomes, safety, and optimal dose of botulinum toxin for OAB.
Conflict of interest statement
None known
Figures
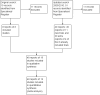


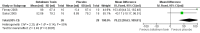


Update of
-
Botulinum toxin injections for adults with overactive bladder syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jul 18;(3):CD005493. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005493.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Dec 07;(12):CD005493. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005493.pub3. PMID: 17636801 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Brubaker 2008 {published data only}
-
- Brubaker L. Refractory urge urinary incontinence and botulinum A injection: The methods of the RUBI trial. Journal of Applied Research 2006;6(4):260‐71.
-
- Brubaker L, Pelvic Floor Disorders Network. Refractory urge urinary incontinence and botulinum A toxin injection trial (Abstract number 101). Neurourology & Urodynamics 2007;26(5):728.
-
- Brubaker L, Pelvic Floor Disorders Network (PFDN). Refractory urge urinary incontinence and botulinum A toxin injection (RUBI) trial (Abstract number 2 Oral). Journal of Pelvic Medicine & Surgery 2007;13(5):224‐5.
Ehren 2007 {published data only}
-
- Ehren I, Volz D, Farrelly E, Berglund L, Brundin L, Hultling C, et al. Efficacy and impact of botulinum toxin A on quality of life in patients with neurogenic detrusor overactivity. Scandinavian Journal of Urology & Nephrology 2007;41(4):335‐40. - PubMed
Finney 2006 {published data only}
-
- Finney S, Patrick K, Stewart L. A double‐blind, placebo controlled study investigating efficacy of botulinum toxin type A (Dysport ‐ trademark) in MS related overactive bladder syndrome (OAB): provisional 36 week results (Abstract number 130). Neurourology & Urodynamics 2006;25(6):663‐4.
Flynn 2009 {published data only}
-
- Flynn M, Amundsen C, Webster G. Short‐term outcomes of a randomized, double‐blind placebo controlled trial of botulinum A toxin for the management of severe idiopathic detrusor overactivity incontinence (Abstract number 3 Oral). Journal of Pelvic Medicine & Surgery 2007;13(5):225‐6.
-
- Flynn M, Amundsen C, Webster G. Short‐term outcomes of a randomized, double‐blind placebo controlled trial of botulinum A toxin for the management of severe idiopathic detrusor overactivity incontinence (Abstract number 317). Proceedings of the 37th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society (ICS), 20‐24 Aug, Rotterdam, the Netherlands. 2007.
-
- Flynn M, Amundsen C, Webster G. Short‐term outcomes of a randomized, double‐blind placebo controlled trial of botulinum A toxin for the management of severe idiopathic detrusor overactivity incontinence (Abstract number 317). Proceedings of the 37th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society (ICS), 20‐24 Aug, Rotterdam, the Netherlands. 2007.
Ghei 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ghei M, Maraj B, Miller R, Nathan S, O'Sullivan C, Fowler CJ, et al. Effects of botulinum toxin B on refractory detrusor overactivity: a randomised, double blind, placebo controlled, crossover trial. The Journal of Urology 2005;174(5):972‐6. - PubMed
-
- Ghei M, Maraj BH, Miller R, Nathan S, O'Sullivan C, Fowler CJ, et al. Effects of botulinum toxin B on refractory detrusor overactivity: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo controlled, crossover trial. Journal of Urology 2005;174(5):1873‐1877; discussion 1877. - PubMed
Giannantoni 2004 {published data only}
-
- Giannantoni A, Stasi SM, Stephen RL, Bini V, Costantini E, Porena M. Intravesical resiniferatoxin versus botulinum‐A toxin injections for neurogenic detrusor overactivity: a prospective randomised study. The Journal of Urology 2004;172(1):240‐3. [19320] - PubMed
Gousse 2005 {published data only}
-
- Caruso D, Kanagarajah P, Gousse A. 100 vs. 150 units of intra‐detrusor Botox (trademark): dose differences in OAB‐wet patients? (Abstract number 316). Proceedings of the 39th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society (ICS), 2009 Sep 29 ‐ Oct 3, San Francisco, CA. 2009.
-
- Cohen BL, Barboglio P, Rodriguez D, Gousse AE. Preliminary results of a dose‐finding study for botulinum toxin‐A in patients with idiopathic overactive bladder: 100 versus 150 units. Neurourology & Urodynamics 2009;28(3):205‐8. - PubMed
-
- Cohen BL, Rivera R, Barboglio P, Gousse A. Safety and tolerability of sedation‐free flexible cystoscopy for intradetrusor botulinum toxin‐A injection. Journal of Urology 2007;177(3):1006‐10; discussion 1010. - PubMed
-
- Gousse A, Barboglio P, Cohen B, Rodriguez D, Caruso D. Botox (R) for idiopathic overactive bladder patients refractory to antimuscarinic therapy in the absence of detrusor overactivity (Abstract number 133). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2008;27(7):724‐5.
-
- Gousse A, Barboglio P, Cohen B, Rodriguez D, Caruso D. Can we predict who will respond to botulinum toxin‐A injections for idiopathic overactive bladder? (Abstract number 538). Proceedings of the 38th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society (ICS), 20‐24 Oct, Cairo, Egypt. 2008.
Grise 2008 {published data only}
-
- Grise P, Ruffion A, Chartier‐Kastler E, Denys P, Egon G. Impact on continence of only bladder botulinum toxin injection without antimuscarinics in neurogenic patients (Abstract number 356). Proceedings of the 38th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society (ICS), 20‐24 Oct, Cairo, Egypt. 2008.
Herschorn 2009 {published data only}
-
- Herschorn S, Gajewski J, Ethans K, Corcos J, Carlson K, Bailly G, et al. Botulinum toxin A in patients with neurogenic detrusor overactivity: preliminary results from a Canadian multicentre randomized trial (Abstract number: Poster# 50). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2009;28(2):138‐9.
-
- Herschorn S, Gajewski J, Ethans K, Corcos J, Carlson K, Bailly G, et al. Efficacy of botulinum toxin A injection for neurogenic detrusor overactivity and urinary incontinence ‐ a randomized double‐blind trial (Abstract number 33). Neurourology & Urodynamics 2009;28(7):608‐9. - PubMed
Karsenty 2005 {published data only}
-
- Karsenty G, Boy S, Reitz A, et al. Botulinum toxin‐A (BTA) in the treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity incontinence (NDOI)‐a prospective randomized study to compare 30 vs. 10 injection sites (abstract). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2005;24(5/6):547‐8. [20977]
King 2007 {published data only}
-
- King J, Neville J. A randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial of botulinum toxin type A injections for the treatment of refractory idiopathic detrusor overactivity. International Urogynecology Journal & Pelvic Floor Dysfunction 2007;18(Suppl 1):S77.
Kuo 2006 {published data only}
-
- Kuo H, Liu H. Will suburothelial injection of different dose of botulinum A toxin have similar therapeutic effects and less adverse events for refractory detrusor overactivity? (Abstract number 145). Proceedings of the 36th Annual Meeting of the ICS, 2006, 27 Nov‐1 Dec, Christchurch, New Zealand. 2006.
-
- Kuo HC. Will suburothelial injection of small dose of botulinum A toxin have similar therapeutic effects and less adverse events for refractory detrusor overactivity?. Urology 2006;68(5):993‐997, discussion 997‐8. - PubMed
Kuo 2007 {published data only}
-
- Kuo H‐C. Comparative study of the therapeutic effects of different intravesical injections of botulinum toxin A on overactive bladder (Poster abstract number 1190). Journal of Urology 2007;177(4 Suppl S).
-
- Kuo HC. Comparison of effectiveness of detrusor, suburothelial and bladder base injections of botulinum toxin a for idiopathic detrusor overactivity. Journal of Urology 2007;178(4 Pt 1):1359‐63. - PubMed
Lucioni 2008 {published data only}
-
- Lucioni A, Rapp DE, Reynolds WS, Gong EM, Fedunok PA, Bales GT. Evaluation of the effect of injection volumes of intravesical botulinum‐A toxin injections in patients with overactive bladder symptoms (Abstract number 17). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2008;27(2):132.
Moore 2009 {published data only}
-
- Moore KM, Hirst G, Emery S, Turner A, Lucas M. A double blind, placebo controlled, randomised, cross over study of trigone specific injections of botulinum toxin B for treating patients with idiopathic detrusor overactivity refractory to other conservative treatments (Abstract number 209). Neurourology & Urodynamics 2009;28(7):833‐4.
Sahai 2005 {published data only}
-
- Sahai A, Dowson C, Khan MS, Dasgupta P. Improvement in quality of life after botulinum toxin‐A injections for idiopathic detrusor overactivity: results from a randomized double‐blind placebo‐controlled trial. BJU International 2009;103(11):1509‐15. - PubMed
-
- Sahai A, Khan M, Smith K, Dasgupta P. Botulinum toxin‐A for patients with idiopathic detrusor overactivity: early results from a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Proceedings of the 35th Annual International Continence Society (ICS); 2005 Aug 28 ‐ Sept 2; Montreal. 2005:Abstract 428. [21092]
-
- Sahai A, Khan MS, Dasgupta P. Efficacy of botulinum toxin‐A for treating idiopathic detrusor overactivity: results from a single center, randomized, double‐blind, placebo controlled trial. Journal of Urology 2007;177(6):2231‐6. - PubMed
-
- Sahai A, Khan S, Dasgupta P. Quality of life in patients with symptoms of overactive bladder and refractory idiopathic detrusor over activity following intradetrusor injections of botulinum toxin type A: results from a randomised, double blind, placebo‐controlled trial (Abstract number 675). European Urology Supplements 2006;5:191.
Schurch 2005 {published data only}
-
- Schurch B. Botulinum toxin in the treatment of neurogenic bladder in adults and children. European Urology, Supplements 2006;5(11):679‐84.
-
- Schurch B, Seze M, Denys P, Chartier‐Kastler E, Haab F, Everaert K, et al. Botulinum toxin type A is a safe and effective treatment for neurogenic urinary incontinence: results of a single treatment, randomised, placebo controlled 6‐month study. The Journal of Urology 2005;174(1):196‐200. [20654] - PubMed
-
- Schurch B, Seze M, Denys P, Chartier‐Kastler E, Haab F, Evereart K, et al. Subgroup analysis to determine impact of patient demographics on urodynamic response to focal administration of botulinum toxin A. Neurourology & Urodynamics 2005;24(5/6):545‐6.
-
- Schurch B, Denys P, Kozma CM, Reese PR, Slaton T, Barron RL. Botulinum toxin a improves the quality of life of patients with neurogenic urinary incontinence. European Urology 2007;52(3):850‐9. - PubMed
Thavaseelan 2005 {published data only}
-
- Thavaseelan J T, Burns‐Cox N, Jordan K, Trewhella J. Efficacy of botulinum toxin type A (BOTOX) in the management of the neurogenic bladder: a prospective, randomised, double blind, dose comparative trial ‐ interim overview of results. British Journal of Urology 2005;95 Suppl 1:4‐5. [21155]
Truzzi 2004 {published data only}
-
- Truzzi J, Bruschini H, Simonetti R, Miguel S. What is the best dose for intravesical botulinum‐A toxin injected in overactive bladder treatment? A prospective randomised preliminary study. Proceedings of the International Continence Society (34th Annual Meeting), and the International Urogynaecological Association; 2004 Aug 23‐27; Paris. 2004:Abstract 520. [19069]
References to studies excluded from this review
Brubaker 2006 {published data only}
-
- Brubaker L. Refractory urge urinary incontinence and botulinum A injection: The methods of the RUBI trial. Journal of Applied Research 2006;6(4):260‐71.
Brubaker 2007 {published data only}
-
- Brubaker L, Pelvic Floor Disorders Network (PFDN). Refractory urge urinary incontinence and botulinum A toxin injection (RUBI) trial (Abstract number 2 Oral). Journal of Pelvic Medicine & Surgery 2007;13(5):224‐5.
Brubaker 2007a {published data only}
-
- Brubaker L, Pelvic Floor Disorders Network. Refractory urge urinary incontinence and botulinum A toxin injection trial (Abstract number 101). Neurourology & Urodynamics 2007;26(5):728.
Caruso 2009 {published data only}
-
- Caruso D, Kanagarajah P, Gousse A. 100 vs. 150 units of intra‐detrusor Botox (trademark): dose differences in OAB‐wet patients? (Abstract number 316). Proceedings of the 39th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society (ICS), 2009 Sep 29 ‐ Oct 3, San Francisco, CA 2009.
Cohen 2007 {published data only}
-
- Cohen BL, Rivera R, Barboglio P, Gousse A. Safety and tolerability of sedation‐free flexible cystoscopy for intradetrusor botulinum toxin‐A injection. Journal of Urology 2007;177(3):1006‐1010; discussion 1010. - PubMed
Cohen 2008 {published data only}
-
- Cohen BL, Barboglio P, Gousse AE. Can we predict who will respond to botulinum toxin‐A injections for idiopathic overactive bladder? (Abstract number 18). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2008;27(2):132‐3.
Cohen 2009 {published data only}
-
- Cohen BL, Barboglio P, Rodriguez D, Gousse AE. Preliminary results of a dose‐finding study for botulinum toxin‐A in patients with idiopathic overactive bladder: 100 versus 150 units. Neurourology & Urodynamics 2009;28(3):205‐8. - PubMed
Cohen 2009a {published data only}
Cui 2007 {published data only}
-
- Cui X‐G, Qu C‐Y, Xu D‐F, Ren J‐Z, Kong L‐L, Lin H‐Y. Botulinum toxin injection into urethral external sphincter combined with oral baclofen in treatment of patients with detrusor‐external sphincter dyssynergia after spinal cord injury. Academic Journal of Second Military Medical University 2007;28(8):875‐7.
de Seze 2002 {published data only}
-
- Seze M, Petit H, Gallien P, Seze MP, Joseph PA, Mazaux JM, Barat M. Botulinum A toxin and detrusor dyssynergia: A double‐blind lidocaine‐controlled study in 13 patients with spinal cord disease. European Urology 2002;42(1):56‐62. [15931] - PubMed
Dykstra 1990 {published data only}
-
- Dykstra DD, Sidi AA. Treatment of detrusor‐sphincter dyssynergia with botulinum A toxin: a double‐blind study. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1990;71(1):24‐6. [384] - PubMed
Farid 2009 {published data only}
-
- Farid M, Youssef T, Mahdy T, Omar W, Moneim HA, Nakeeb A, et al. Comparative study between botulinum toxin injection and partial division of puborectalis for treating anismus. International Journal of Colorectal Disease 2009;24(3):327‐34. - PubMed
Farid 2009a {published data only}
-
- Farid M, Monem HA, Omar W, Nakeeb A, Fikry A, Youssef T, et al. Comparative study between biofeedback retraining and botulinum neurotoxin in the treatment of anismus patients. International Journal of Colorectal Disease 2009;24(1):115‐20. - PubMed
Flynn 2007 {published data only}
-
- Flynn M, Amundsen C, Webster G. Short‐term outcomes of a randomized, double‐blind placebo controlled trial of botulinum A toxin for the management of severe idiopathic detrusor overactivity incontinence (Abstract number 3 Oral). Journal of Pelvic Medicine & Surgery 2007;13(5):225‐6.
Flynn 2007a {published data only}
-
- Flynn M, Amundsen C, Webster G. Short‐term outcomes of a randomized, double‐blind placebo controlled trial of botulinum A toxin for the management of severe idiopathic detrusor overactivity incontinence (Abstract number 317). Proceedings of the 37th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society (ICS), 20‐24 Aug, Rotterdam, The Netherlands. 2007.
Flynn 2008 {published data only}
-
- Flynn M, Amundsen C, Perevich M, Webster G. Short‐term outcomes of a randomized, double‐blind placebo controlled trial of botulinum A toxin for the management of severe idiopathic detrusor overactivity incontinence (Abstract number 33, poster). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2008;27(2):151‐2.
Gallien 2005 {published data only}
-
- Gallien P, Reymann JM, Amarenco G, Nicolas B, Seze M, Bellissant E. Placebo controlled, randomised, double blind study of the effects of botulinum A toxin on detrusor sphincter dyssynergia in multiple sclerosis patients. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry 2005;76(12):1670‐6. - PMC - PubMed
Ghei 2005a {published data only}
-
- Ghei M, Maraj BH, Miller R, Nathan S, O'Sullivan C, Fowler CJ, et al. Effects of botulinum toxin B on refractory detrusor overactivity: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo controlled, crossover trial. Journal of Urology 2005;174(5):1873‐1877; discussion 1877. - PubMed
Ghei 2006 {published data only}
-
- Ghei M, Maraj BH, Nathan S, Malone‐Lee J, Miller R. Autonomic side effects of Botulinum toxin Type B Intravesical injections: Report of 4 cases and review of the literature. International Urology & Nephrology 2006;38(3‐4):543‐4. - PubMed
Giannantoni 2003 {published data only}
-
- Giannantoni A, Stasi SM, Pizzirusso G, Mearini E, Bini V, Porena M. Intravesical resiniferatoxin versus botulinum‐A toxin injections for the treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity (Abstract). Neurourology & Urodynamics 2003;22(5):497. [17103]
Giannantoni 2004B {published data only}
-
- Giannantoni A, Mearini E, Stasi SM, Constantini E, Zucchi A, Mearini L, et al. New therapeutic options for refractory detrusor overactivity. Minerva Urologica e Nefrologica 2004;56(1):79‐87. [20255] - PubMed
Gousse 2005 B {published data only}
-
- Gousse A, Tunuguntla H, Rodriguez D, Velasquez D. Validated instrument to assess pain tolerance during flexible endoscopy for intradetrusor botox‐A injection (Abstract number 520). Proceedings of the 35th Annual International Continence Society (ICS); 2005 Aug 28 ‐ Sept 2; Montreal. 2005. [21070]
Gousse 2005a {published data only}
-
- Gousse AE, Tununguntia HSGR, Bateman D, Velasquez D. Dose‐finding prospective randomized study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of botulinum‐A toxin for refractory non‐neurogenic overactive bladder (Abstract). Neurourology & Urodynamics 2005;24(2):161.
Gousse 2007 {published data only}
-
- Gousse AE, Cohen B, Rodriguez D, Barboglio PG. Scheduled repeated Botox (trademark) injections for idiopathic OAB: evaluating therapeutic time (Poster abstract number 1192). Journal of Urology 2007;177(4 Suppl S):39.
Gousse 2007a {published data only}
-
- Gousse AE, Barboglio P, Rivera R, Tunuguntla H, Cason L. Repeat Botox A injections and urodynamic findings in neurogenic OAB: long‐tem results (Abstract number 20). Neurourology & Urodynamics 2007;26(7 Suppl):1071.
Gousse 2007b {published data only}
-
- Gousse A, Cohen B, Rodriguez D, Barboglio P. Botulinum toxin A: intradetrusor re‐injections in idiopathic overactive bladder every 6 months ‐ 3 years follow up (Abstract number 102). Neurourology & Urodynamics 2007;26(5):728‐9.
Gousse 2007c {published data only}
-
- Gousse A, Cohen B, Rodriguez D, Barboglio P. Botulinum toxin A 100 vs 150 units in idiopathic overactive bladder patients: is there any difference? (Abstract number 100). Neurourology & Urodynamics 2007;26(5):726‐7. - PubMed
Gousse 2007d {published data only}
-
- Gousse A, Rivera R, Tunuguntla H, Barboglio P. Repeated intradetrusor injections of botulinum toxin‐A in neurogenic overactive bladder: urodynamic, UDI‐6 and quality of life data (Abstract number 103). Neurourology & Urodynamics 2007;26(5):730‐1.
Gousse 2008 {published data only}
-
- Gousse A, Barboglio P, Cohen B, Rodriguez D, Caruso D. The need for intermittent catheterization during repeated Botox (trademark) injections for idiopathic OAB (Abstract number 417). Proceedings of the 38th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society (ICS), 20‐24 Oct, Cairo, Egypt. 2008.
Gousse 2008a {published data only}
-
- Gousse A, Barboglio P, Cohen B, Rodriguez D, Caruso D. Can we predict who will respond to botulinum toxin‐A injections for idiopathic overactive bladder? (Abstract number 538). Proceedings of the 38th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society (ICS), 20‐24 Oct, Cairo, Egypt. 2008.
Gousse 2008b {published data only}
-
- Gousse A, Barboglio P, Cohen B, Rodriguez D, Caruso D. Botox (R) for idiopathic overactive bladder patients refractory to antimuscarinic therapy in the absence of detrusor overactivity (Abstract number 133). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2008;27(7):724‐5.
Gousse 2009 {published data only}
-
- Gousse A, Shirodkar S, Gomez C, Kanagarajah P, Barboglio P, Caruso D. Botox (trademark) for idiopathic overactive bladder patients refractory to antimuscarinic therapy in the absence of urodynamically demonstrable detrusor overactivity (Abstract number: Poster# 64). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2009;28(2):144‐5.
Herschorn 2009a {published data only}
-
- Herschorn S, Gajewski J, Ethans K, Corcos J, Carlson K, Bailly G, et al. Botulinum toxin A in patients with neurogenic detrusor overactivity: preliminary results from a Canadian multicentre randomized trial (Abstract number: Poster# 50). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2009;28(2):138‐9.
Keshtgar 2007 {published data only}
-
- Keshtgar AS, Ward HC, Sanei A, Clayden GS. Botulinum toxin, a new treatment modality for chronic idiopathic constipation in children: long‐term follow‐up of a double‐blind randomized trial. Journal of Pediatric Surgery 2007;42(4):672‐80. - PubMed
Kessler 2007 {published data only}
-
- Kessler TM. Words of wisdom. Re: Efficacy of botulinum toxin‐A for treating idiopathic detrusor overactivity: results from a single center, randomized, double‐blind, placebo controlled trial. European Urology 2007;52(6):1793‐4. - PubMed
Kuo 2006a {published data only}
-
- Kuo HC. Will suburothelial injection of small dose of botulinum A toxin have similar therapeutic effects and less adverse events for refractory detrusor overactivity?. Urology 2006;68(5):993‐997, discussion 997‐8. - PubMed
Kuo 2007a {published data only}
-
- Kuo H‐C. Comparison of the therapeutic effects of urethral injections of 50 and 100 units of botulinum A toxin for voiding dysfunction. Tzu Chi Medical Journal 2007;19(3):134‐8.
Kuo 2007b {published data only}
-
- Kuo HC. Recovery of detrusor function after urethral botulinum A toxin injection in patients with idiopathic low detrusor contractility and voiding dysfunction. Urology 2007;69(1):57‐61, discussion 61‐2. - PubMed
Kuo 2007c {published data only}
-
- Kuo HC. Comparison of effectiveness of detrusor, suburothelial and bladder base injections of botulinum toxin a for idiopathic detrusor overactivity. Journal of Urology 2007;178(4 Pt 1):1359‐63. - PubMed
Maria 1998 {published data only}
-
- Maria G, Cassetta E, Gui D, Brisinda G, Bentivoglio AR, Albanese A. A comparison of botulinum toxin and saline for the treatment of chronic anal fissure. New England Journal of Medicine 1998;338:217‐20. [5285] - PubMed
Maria 2003 {published data only}
-
- Maria G, Brisinda G, Civello IM, Bentivoglio AR, Sganga G, Albanese A. Relief by botulinum toxin of voiding dysfunction due to benign prostatic hyperplasia: results of a randomized, placebo‐controlled study. Urology 2003;62(2):259‐64. [16639] - PubMed
Neel 2007 {published data only}
-
- Neel KF, Soliman S, Salem M, Seida M, Al Hazmi H, Khatab A. Botulinum‐A toxin: solo treatment for neuropathic noncompliant bladder. Journal of Urology 2007;178(6):2593‐2597; discussion 2597‐8. - PubMed
Ron 2001 {published data only}
-
- Ron Y, Avni Y, Lukovetski A, Wardi J, Geva D, Birkenfeld S, Halpern Z. Botulinum toxin type‐a in therapy of patients with anismus. Diseases of the Colon & Rectum 2001;44(12):1821‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sahai 2006 {published data only}
-
- Sahai A, Khan S, Dasgupta P. Quality of life in patients with symptoms of overactive bladder and refractory idiopathic detrusor over activity following intradetrusor injections of botulinum toxin type A: results from a randomised, double blind, placebo‐controlled trial (Abstract number 675). European Urology Supplements 2006;5:191.
Sahai 2007 {published data only}
-
- Sahai A, Khan MS, Dasgupta P. Efficacy of botulinum toxin‐A for treating idiopathic detrusor overactivity: results from a single center, randomized, double‐blind, placebo controlled trial. Journal of Urology 2007;177(6):2231‐6. - PubMed
Sahai 2009 {published data only}
-
- Sahai A, Dowson C, Khan MS, Dasgupta P. Improvement in quality of life after botulinum toxin‐A injections for idiopathic detrusor overactivity: results from a randomized double‐blind placebo‐controlled trial. BJU International 2009;103(11):1509‐15. - PubMed
Schurch 2004 {published data only}
-
- Schurch B, Reitz A, Tenti G. Electromotive drug administration of lidocaine to anaesthetise the bladder before botulinum‐A toxin injections into the detrusor. Spinal Cord 2004;42(6):338‐41. [19336] - PubMed
Schurch 2004 B {published data only}
-
- Schurch B, Seze M, Denys P, Chartier‐Kastler E, Ismael S, Haab F, et al. Botulinum toxin A in neurogenic urinary incontinence: results from a multi‐centre randomised, controlled trial (abstract). Neurourology & Urodynamics 2004;23(5/6):609‐10. [MEDLINE: ]
Schurch 2005 B {published data only}
-
- Schurch B, Seze M, Denys P, Chartier‐Kastler E, Haab F, Evereart K, et al. Subgroup analysis to determine impact of patient demographics on urodynamic response to focal administration of botulinum toxin A. Neurourology & Urodynamics 2005;24(5/6):545‐6.
Schurch 2006 {published data only}
-
- Schurch B. Botulinum toxin in the treatment of neurogenic bladder in adults and children. European Urology, Supplements 2006;5(11):679‐84.
Schurch 2007 {published data only}
-
- Schurch B, Denys P, Kozma CM, Reese PR, Slaton T, Barron RL. Botulinum toxin a improves the quality of life of patients with neurogenic urinary incontinence. European Urology 2007;52(3):850‐9. - PubMed
Taha 2007 {published data only}
-
- Taha M, Farahat Y, Bahnasy A, Damhougy M. A randomized controlled trial of bacillus calmette‐guerin and botulinum toxin‐A for the treatment of refractory interstitial cystitis (Abstract number 107). Neurourology & Urodynamics 2007;26(5):735.
Additional references
Alhasso 2009
Apostolidis 2006
-
- Apostolidis A, Dasgupta P, Fowler C. Proposed mechanism for the efficacy of injected botulinum toxin in the treatment of human detrusor overactivity. European Urology 2006;49:644‐50. - PubMed
Coyne 2009
-
- Coyne K, Wein A, Tubaro A, Sexton C, Thompson C, Kopp S, Aiyer L. The burden of lower urinary tract symptoms: evaluating the effects of LUTS on health‐related quality of life, anxiety and depression: EpiLUTS. BJU International 2009;103(supplement 3):4‐11. - PubMed
Cruz 2004
-
- Cruz F. Mechanisms involved in new therapies for overactive bladder. Urology 2004 March;63(supplement 3A):65‐73. - PubMed
Drake 2008
-
- Drake M. Mechanisms of action of intravesical botulinum treatment in refractory detrusor overactivity. BJU International 2008;102(Supplement 1):11‐6. - PubMed
Eustice 2000
Hay‐Smith 2009
Herbison 2009
ICS 2005
-
- International Continence Society. Fact Sheet 2: Overactive Bladder. www.icsoffice.org July 2005.
Irwin 2006
-
- Irwin DE, Milsom I, Hunskaar S, Reilly K, Kopp Z, Herschorn S, et al. Population‐based survey of urinary incontinence, overactive bladder, and other lower urinary tract symptoms in five countries: results of the EPIC study. European Urology 2006 Dec;50(6):1306‐14. - PubMed
Irwin 2008
-
- Irwin DE, Mungapen L, Milsom I, Kopp Z, Reeves P, Kelleher C. The economic impact of overactive bladder syndrome in six western countries. BJU International 2008;103:202‐9. - PubMed
Nabi 2006
Ostaszkiewicz 2004a
Ostaszkiewicz 2004b
Roxburgh 2009
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

