Bisphosphonates for osteoporosis in primary biliary cirrhosis
- PMID: 22161446
- PMCID: PMC12448277
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009144.pub2
Bisphosphonates for osteoporosis in primary biliary cirrhosis
Abstract
Background: Bisphosphonates are widely used for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Patients with primary biliary cirrhosis often have osteoporosis - either postmenopausal or secondary to the liver disease. No systematic review or meta-analysis has assessed the effects of bisphosphonates for osteoporosis in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis.
Objectives: To assess the beneficial and harmful effects of bisphosphonates for osteoporosis in primary biliary cirrhosis.
Search methods: The Cochrane Hepato-Biliary Group Controlled Trials Register, The Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) in The Cochrane Library, MEDLINE, EMBASE, Science Citation Index Expanded, LILACS, clinicaltrials.gov, the WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform, and full text searches were conducted until November 2011. Manufacturers and authors were contacted for additional studies during the conductance of the review.
Selection criteria: All randomised clinical trials of bisphosphonates in primary biliary cirrhosis compared with placebo or no intervention, or another bisphosphonate, or any other drug.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors extracted data. RevMan Analysis was used for statistical analysis of dichotomous data with risk ratio (RR) or risk difference (RD) and of continuous data with mean difference (MD) or standardised mean difference (SMD), all with 95% confidence intervals (CI). Methodological components were used to assess risk of systematic errors (bias). Trial sequential analysis was also used to control for random errors (play of chance).
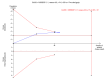
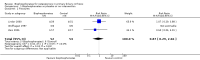
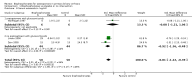
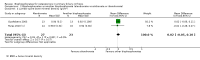
Main results: Six trials were included. Three trials with 106 participants, of which two trials with high risk of bias, did not demonstrate significant effects of bisphosphonates (etidronate or alendronate) versus placebo or no intervention regarding mortality (RD 0.00; 95% CI -0.12 to 0.12, I² = 0%), fractures (RR 0.87; 95% CI 0.29 to 2.66, I² = 0%), or adverse events (RR 1.00; 95% CI 0.49 to 2.04). Two trials with 62 participants with high risk of bias compared one bisphosphonate (etidronate or alendronate) versus another (alendronate or ibandronate) and found no significant difference regarding mortality (RD -0.03; 95% CI -0.14 to 0.07, I² = 0%), fractures (RR 0.95; 95% CI 0.18 to 5.06, I² = 0%), or adverse events (RR 1.00; 95% CI 0.49 to 2.04, I² = 0%). Bisphosphonates had no significant effect on liver-related mortality, liver transplantation, or liver-related morbidity compared with placebo or no intervention, or another bisphosphonate. Bisphosphonates had no significant effect on bone mineral density compared with placebo or no intervention, or another bisphosphonate. Bisphosphonates compared with placebo or no intervention seem to decrease the urinary amino telopeptides of collagen I (NTx) concentration (MD -16.93 nmol bone collagen equivalents/mmol creatinine; 95% CI -23.77 to -10.10; 2 trials with 88 patients; I² = 0%) and serum osteocalcin (SMD -0.81; 95% CI -1.22 to -0.39; 3 trials with 100 patients; I² = 34 %) concentration. The former result was supported by trial sequential analysis, but not the latter. Alendronate compared with another bisphosphonate (ibandronate) had no significant effect on serum osteocalcin concentration (MD -3.61 ng/ml, 95% CI -9.41 to 2.18; 2 trials with 47 patients; I² = 82%) in a random-effects meta-analysis, but it significantly decreased serum osteocalcin (MD -4.40 ng/ml, 95% CI -6.75 to -2.05; 2 trials with 47 patients; I² = 82%), the procollagen type I N-terminal propeptide (MD -8.79 ng/ml, 95% CI -15.96 to -1.63; 2 trials with 47 patients; I² = 38%), and NTx concentration (MD -14.07 nmol bone collagen equivalents/mmol creatinine, 95% CI -24.23 to -3.90; 2 trials with 46 patients; I²=0%) in a fixed-effect model. The latter two results were not supported by trial sequential analyses. There was no statistically significant difference in the number of patients having bisphosphonates withdrawn due to adverse events compared with placebo or no intervention (RD -0.04; 95% CI -0.21 to 0.12; 2 trials with 46 patients; I² = 0%), or another bisphosphonate (RR 0.56; 95% CI 0.14 to 2.17; 2 trials with 62 patients; I² = 0%). One trial with 32 participants and with high risk of bias compared etidronate versus sodium fluoride without finding significant difference regarding mortality, fractures, adverse events, or bone mineral density. Etidronate compared with sodium fluoride significantly decreased serum osteocalcin, urinary hydroxyproline, and parathyroid hormone concentration.
Authors' conclusions: We did not find evidence to support or refute the use of bisphosphonates for patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. The data seem to indicate a possible positive intervention effect of bisphosphonates on decreasing urinary amino telopeptides of collagen I concentration compared with placebo or no intervention with no risk of random error. There is need for more randomised clinical trials assessing the effects of bisphosphonates for osteoporosis on patient-relevant outcomes in primary biliary cirrhosis.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures

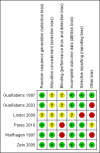
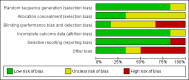
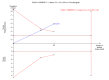
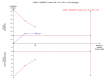


















Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009144
References
References to studies included in this review
Guañabens 1997 {published data only}
-
- Guanabens N, Pares A. Cyclical etidronate versus sodium fluoride for treatment of osteoporosis in primary biliary cirrhosis. Preliminary results after two years [abstract]. Osteoporos International 1996; Vol. 6, issue Suppl 1:288.
-
- Guañabens N, Parés A, Monegal A, Peris P, Pons F, Alvarez L, et al. Etidronate versus fluoride for treatment of osteopenia in primary biliary cirrhosis: preliminary results after 2 years. Gastroenterology 1997;113(1):219‐24. - PubMed
Guañabens 2003 {published data only}
-
- Guañabens N, Parés A, Ros I, Alvarez L, Pons F, Caballería L, et al. Alendronate is more effective than etidronate for increasing bone mass in osteopenic patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2003;98(10):2268‐74. - PubMed
-
- Pares A, Guanabens N, Ros I, Pons F, Alvarez L, Caballeria L, et al. Alendronate versus Etidronate for osteopenic patients with primary biliary cirrhosis: results after two years of treatment [abstract]. Journal of Hepatology 2001; Vol. 34, issue 1:19.
Lindor 2000 {published data only}
-
- Lindor KD, Jorgensen RA, Tiegs RD, Khosla S, Dickson ER. Etidronate for osteoporosis in primary biliary cirrhosis: a randomized trial. Journal of Hepatology 2000;33(6):878‐82. - PubMed
Pares 2010 {published data only}
-
- Pares A, Cerda D, Monegal A, Muxi A, Caballeria L, Peris P, et al. Monthly ibandronate vs. weekly alendronate in the treatment of osteoporosis associated with primary biliary cirrhosis: Similar efficacy but different adherence. Journal of Hepatology 2010;52(Suppl 1):S79.
Wolfhagen 1997 {published data only}
-
- Wolfhagen FH, Buuren HR, Ouden JW, Hop WC, Leeuwen JP, Schalm SW, et al. Cyclical etidronate in the prevention of bone loss in corticosteroid‐treated primary biliary cirrhosis. A prospective, controlled pilot study. Journal of Hepatology 1997;26(2):325‐30. - PubMed
-
- Wolfhagen FHJ, Ouden JW, Buuren HR, Leeuwen JPTM, Schalm SW, Pols HAP. Cyclical etidronate in the prevention of corticosteroid‐induced bone loss in primary biliary cirrhosis. The Netherlands Journal of Medicine 1995;47:A10.
Zein 2005 {published data only}
-
- Zein CO, Jorgensen RA, Clarke B, Lindor KD. Alendronate improves bone mineral density in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis: randomized placebo‐controlled trial. Gastroenterology 2004; Vol. 126, issue 4:A671. - PubMed
-
- Zein CO, Jorgensen RA, Clarke B, Wenger DE, Keach JC, Angulo P, et al. Alendronate improves bone mineral density in primary biliary cirrhosis: a randomized placebo‐controlled trial. Hepatology 2005;42(4):762‐71. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Crawford 2006 {published data only}
-
- Crawford BA, Kam C, Pavlovic J, Byth K, Handelsman DJ, Angus PW, et al. Zoledronic acid prevents bone loss after liver transplantation ‐ a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Annals of Internal Medicine 2006;144(4):239‐48. - PubMed
Millonig 2005 {published data only}
-
- Millonig G, Graziadei IW, Eichler D, Pfeiffer KP, Finkenstedt G, Muehllechner P, et al. Alendronate in combination with calcium and vitamin D prevents bone loss after orthotopic liver transplantation: a prospective single‐center study. Liver Transplantation 2005;11(8):960‐6. - PubMed
Shiomi 2002 {published data only}
-
- Shiomi S, Nishiguchi S, Kurooka H, Tamori A, Habu D, Takeda T, et al. Cyclical etidronate for treatment of osteopenia in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Hepatology Research 2002;22(2):102‐6. - PubMed
Valero 1995 {published data only}
-
- Valero MA, Loinaz C, Larrodera L, Leon M, Moreno E, Hawkins F. Calcitonin and bisphosphonates treatment in bone loss after liver transplantation. Calcified Tissue International 1995;57(1):15‐9. - PubMed
Additional references
AASLD 2010
-
- Silveira MG, Brunt EM, Heathcote J, Gores GJ, Lindor KD, Mayo MJ. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases endpoints conference: design and endpoints for clinical trials in primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology 2010;52(1):349‐59. - PubMed
Adami 1996
-
- Adami S, Zamberlan N. Adverse effects of bisphosphonates: a comparative review. Drug Safety 1996;14:158‐70. - PubMed
Boulton‐Jones 2004
-
- Boulton‐Jones JR, Fenn RM, West J, Logan RF, Ryder SD. Fracture risk of women with primary biliary cirrhosis: no increase compared with general population controls. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2004;20(5):551‐7. - PubMed
Bounameaux 1983
-
- Bounameaux HM, Schifferli J, Montani JP, Jung A, Chatelanat F. Renal failure associated with intravenous diphosphonates. Lancet 1983;1(8322):471. - PubMed
Brok 2008
-
- Brok J, Thorlund K, Gluud C, Wetterslev J. Trial sequential analysis reveals insufficient information size and potentially false positive results in many meta‐analyses. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2008;61(8):763‐9. - PubMed
Center 1999
-
- Center JR, Nguyen TV, Schneider D, Sambrook PN, Eisman JA. Mortality after all major types of osteoporotic fracture in men and women: an observational study. Lancet 1999;353:878‐82. - PubMed
Chang 2003
-
- Chang JT, Green L, Beitz J. Renal failure with the use of zoledronic acid. New England Journal of Medicine 2003;349(17):1676‐9. - PubMed
Collier 2002
Cooper 1992
-
- Cooper C, Campion G, Melton III LJ. Hip fractures in the elderly: a world‐wide projection. Osteoporosis International 1992;2:285‐9. - PubMed
Cooper 1997
-
- Cooper C. The crippling consequences of fractures and their impact on quality of life. American Journal of Medicine 1997;103(2A):12S‐19S. - PubMed
Cryer 2002
-
- Cryer B, Bauer DC. Oral bisphosphonates and upper gastrointestinal tract problems: what is the evidence?. Mayo Clinic Proceedings 2002;77(10):1031‐43. - PubMed
Cummings 2002
-
- Cummings SR, Karpf DB, Harris F, Genant HK, Ensrud K, LaCroix AZ, et al. Improvement in spine bone density and reduction in risk of vertebral fractures during treatment with antiresorptive drugs. American Journal of Medicine 2002;112(4):281‐9. - PubMed
DeMets 1987
-
- DeMets DL. Methods for combining randomized clinical trials: strengths and limitations. Statistics in Medicine 1987;6(3):341‐50. - PubMed
DerSimonian 1986
-
- DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta‐analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials 1986;7(3):177‐88. - PubMed
Diamond 1989
-
- Diamond TH, Stiel D, Lunzer M, McDowall D, Eckstein RP, Posen S. Hepatic osteodystrophy. Static and dynamic bone histomorphometry and serum bone Gla‐protein in 80 patients with chronic liver disease. Gastroenterology 1989;96(1):213‐21. - PubMed
EASL 2009
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: management of cholestatic liver diseases. Journal of Hepatology 2009;51(2):237‐67. - PubMed
Egger 1997
Egger 2003
-
- Egger M, Juni P, Bartlett C, Holenstein F, Sterne J. How important are comprehensive literature searches and the assessment of trial quality in systematic reviews? Empirical study. Health Technology Assessment 2003;7(1):1‐76. - PubMed
Fleisch 1969
-
- Fleisch H, Russell RG, Francis MD. Diphosphonates inhibit hydroxyapatite dissolution in vitro and bone resorption in tissue culture and in vivo. Science 1969;165(899):1262‐4. - PubMed
Fleisch 1991
-
- Fleisch H. Bisphosphonates: pharmacology and use in the treatment of tumour‐induced hypercalcaemia and metastatic bone disease. Drugs 1991;42:919‐44. - PubMed
Fleisch 1993
-
- Fleisch H. Bisphosphonates in osteoporosis: an introduction. Osteoporosis International 1991;Suppl 3:S3‐S5. - PubMed
Gimsing 2010
-
- Gimsing P, Carlson K, Turesson I, Fayers P, Waage A, Vangsted A, et al. Effect of pamidronate 30 mg versus 90 mg on physical function in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (Nordic Myeloma Study Group): a double‐blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncology 2010;11(10):973‐82. - PubMed
Gluud 2006
-
- Gluud LL. Bias in clinical intervention research. American Journal of Epidemiology 2006;163(6):493‐501. - PubMed
Gluud 2007
-
- Gluud C, Brok J, Gong Y, Koretz RL. Hepatology may have problems with putative surrogate outcome measures. Journal of Hepatology 2007;46(4):734‐42. - PubMed
Gluud 2011
-
- Gluud C, Nikolova D, Klingenberg SL, Alexakis N, Als‐Nielsen B, Colli A, et al. Cochrane Hepato‐Biliary Group. About The Cochrane Collaboration (Cochrane Review Groups (CRGs)). 2011, Issue 4. Art. No.: LIVER.
Guanabens 2003
-
- Guanabens N, Pares A, Ros I, Alvarez L, Pons F, Caballeria L, et al. Alendronate is more effective than etidronate for increasing bone mass in osteopenic patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2003;98(10):2268‐74. - PubMed
Guañabens 2005
-
- Guañabens N, Parés A, Ros I, Caballería L, Pons F, Vidal S, et al. Severity of cholestasis and advanced histological stage but not menopausal status are the major risk factors for osteoporosis in primary biliary cirrhosis. Journal of Hepatology 2005;42(4):573‐7. - PubMed
Guañabens 2010
-
- Guañabens N, Cerdá D, Monegal A, Pons F, Caballería L, Peris P, et al. Low bone mass and severity of cholestasis affect fracture risk in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2010;138(7):2348‐56. - PubMed
Higgins 2002
-
- Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21(11):1539‐58. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hochberg 2002
-
- Hochberg MC, Greenspan S, Wasnich RD, Miller P, Thompson DE, Ross PD. Changes in bone density and turnover explain the reductions in incidence of nonvertebral fractures that occur during treatment with antiresorptive agents. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2002;87(4):1586‐92. - PubMed
Hodgson 1993
-
- Hodgson SF, Dickson ER, Eastell R, Eriksen EF, Bryant SC, Riggs BL. Rates of cancellous bone remodeling and turnover in osteopenia associated with primary biliary cirrhosis. Bone 1993;14(6):819‐27. - PubMed
Hollis 1999
Homik 1999
ICH‐GCP 1997
-
- International Conference on Harmonisation Expert Working Group. International conference on harmonisation of technical requirements for registration of pharmaceuticals for human use. ICH harmonised tripartite guideline. Guideline for good clinical practice1997 CFR & ICH Guidelines. Vol. 1, PA 19063‐2043, USA: Barnett International/PAREXEL, 1997.
Ioannidis 2009
-
- Ioannidis JP. Adverse events in randomized trials: neglected, restricted, distorted, and silenced. Archives of Internal Medicine 2009;169(19):1737‐9. - PubMed
Kanis 1994
-
- Kanis JA. Assessment of fracture risk and its application to screening for postmenopausal osteoporosis: synopsis of a WHO report. WHO Study Group. Osteoporosis International 1994;4(6):368‐81. - PubMed
Kawelke 2008
-
- Kawelke N, Bentmann A, Hackl N, Hager HD, Feick P, Geursen A, et al. Isoform of fibronectin mediates bone loss in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis by suppressing bone formation. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research 2008;23(8):1278‐86. - PubMed
Kjaergard 2001
-
- Kjaergard LL, Villumsen J, Gluud C. Reported methodologic quality and discrepancies between large and small randomized trials in meta‐analyses. Annals of Internal Medicine 2001;135(11):982‐9. - PubMed
Klibanski 2001
-
- Klibanski A, Adams‐Campbell L, Bassford T, Blair SN, Boden SD, Dickersin K, et al. Osteoporosis prevention, diagnosis, and therapy. Journal of the American Medical Association 2001;285:785‐95.
Lewiecki 2010
-
- Lewiecki EM. Bone densitometry and vertebral fracture assessment. Current Osteoporosis Reports 2010;8(3):123‐30. - PubMed
Luxon 2011
-
- Luxon BA. Bone disorders in chronic liver diseases. Current Gastroenterology Reports 2011;13(1):40‐8. - PubMed
Macaskill 2001
-
- Macaskill P, Walter SD, Irwig L. A comparison of methods to detect publication bias in meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2001;20(4):641‐54. - PubMed
McCaughan 1994
-
- McCaughan GW, Feller RB. Osteoporosis in chronic liver disease: pathogenesis, risk factors, and management. Digestive Diseases 1994;12:223‐31. - PubMed
Menon 2001
-
- Menon KV, Angulo P, Weston S, Dickson ER, Lindor KD. Bone disease in primary biliary cirrhosis: independent indicators and rate of progression. Journal of Hepatology 2001;35(3):316‐23. - PubMed
Menschutkin 1865
-
- Menschutkin M. [About the influence of chloracetyls on phosphorous acids] [author's translation] [Über die einwirkung des chloracetyls auf phosphorige säure]. Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie 1865;133:317‐20.
Metcalf 1996
Migliorati 2005
-
- Migliorati CA, Casiglia J, Epstein J, Jacobsen PL, Siegel MA, Woo SB. Managing the care of patients with bisphosphonate‐associated osteonecrosis: an American Academy of Oral Medicine position paper. Journal of the American Dental Association 2005;136(12):1658‐68. - PubMed
Moher 1998
-
- Moher D, Pham B, Jones A, Cook DJ, Jadad AR, Moher M, et al. Does quality of reports of randomised trials affect estimates of intervention efficacy reported in meta‐analyses?. Lancet 1998;352:609‐13. - PubMed
Olivier 2008
-
- Olivier BJ, Schoenmaker T, Mebius RE, Everts V, Mulder CJ, Nieuwkerk KM, et al. Increased osteoclast formation and activity by peripheral blood mononuclear cells in chronic liver disease patients with osteopenia. Hepatology 2008;47(1):259‐67. - PubMed
Papapoulos 1992
-
- Papapoulos SE, Landman JO, Bijvoet OLM, Lowik CWGM, Vlakema R, Oauvels EKJ, et al. The use of bisphosphonates in the treatment of osteoporosis. Bone 1992;13(SuppI 1):S41‐S49. - PubMed
Pares 2006
-
- Pares A, Guanabens N. Treatment of bone disorders in liver disease. Journal of Hepatology 2006;45(3):445‐53. - PubMed
Reid 2002
-
- Reid IR, Brown JP, Burckhardt P, Horowitz Z, Richardson P, Trechsel U, et al. Intravenous zoledronic acid in postmenopausal women with low bone mineral density. New England Journal of Medicine 2002;346:653‐61. - PubMed
RevMan 2011 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.1. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Rouillard 2001
-
- Rouillard S, Lane NE. Hepatic osteodystrophy. Hepatology 2001;33(1):301‐7. - PubMed
Royle 2003
-
- Royle P, Milne R. Literature searching for randomized controlled trials used in Cochrane reviews: rapid versus exhaustive searches. International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care 2003;19(4):591‐603. - PubMed
Russell 2006
-
- Russell RG. Bisphosphonates: from bench to bedside. Annals NewYork Academy of Sciences 2006;1068:367‐401. - PubMed
Russell 2011
-
- Russell RG. Bisphosphonates: the first 40 years. Bone 2011;49(1):2‐19. - PubMed
Saag 1998
-
- Saag KG, Emkey R, Schnitzer TJ, Brown JP, Hawkins F, Goemaere S, et al. Alendronate for the prevention and treatment of glucocorticoid‐induced osteoporosis. New England Journal of Medicine 1998;339(5):292‐9. - PubMed
Sambrook 2006
-
- Sambrook P, Cooper C. Osteoporosis. Lancet 2006;37 :2010‐8. - PubMed
Schulz 1995
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias. Dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. Journal of the American Medical Association 1995;273(5):408‐12. - PubMed
Smith 2006
-
- Smith DL, Shire NJ, Watts NB, Schmitter T, Szabo G, Zucker SD. Hyperbilirubinemia is not a major contributing factor to altered bone mineral density in patients with chronic liver disease. Journal of Clinical Densitometry 2006;9(1):105‐13. - PubMed
Solaymani‐Dodaran 2006
-
- Solaymani‐Dodaran M, Card TR, Aithal GP, West J. Fracture risk in people with primary biliary cirrhosis: a population‐based cohort study. Gastroenterology 2006;131(6):1752‐7. - PubMed
Strampel 2007
-
- Strampel W, Emkey R, Civitelli R. Safety considerations with bisphosphonates for the treatment of osteoporosis. Drug Safety 2007;30(9):755‐63. - PubMed
Thompson 2002
-
- Thompson SG, Higgins JP. How should meta‐regression analyses be undertaken and interpreted?. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21(11):1559‐73. - PubMed
Thorlund 2009
-
- Thorlund K, Devereaux PJ, Wetterslev J, Gyuatt G, Ioannidis JPA, Thabane L, et al. Can trial sequential monitoring boundaries reduce spurious inferences from meta‐analyses?. International Journal of Epidemiology 2009;38:276‐86. - PubMed
Wariaghli 2010
-
- Wariaghli G, Allali F, Maghraoui A, Hajjaj‐Hassouni N. Osteoporosis in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. European Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2010;22(12):1397‐401. - PubMed
Wasnich 2000
-
- Wasnich RD, Miller PD. Antifracture efficacy of antiresorptive agents are related to changes in bone density. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2000;85(1):231‐6. - PubMed
Wells 2008a
Wells 2008b
Wells 2008c
Wetterslev 2008
-
- Wetterslev J, Thorlund K, Brok J, Gluud C. Trial sequential analysis may establish when firm evidence is reached in cumulative meta‐analysis. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2008;61(1):64‐75. - PubMed
Wetterslev 2009
WHO 1994
-
- World Health Organization Study Group. Assessment of fracture risk and its application to screening for postmenopausal osteoporosis. World Health Organization Technical Report Series 1994;843:1‐129. - PubMed
WHO 2009
-
- World Health Organization. FRAX WHO Fracture Risk Assessment Tool. www.shef.ac.uk/FRAX/ (accessed 10 February 2011).
Wolfhagen 2000
-
- Wolfhagen FH, Buuren HR, Vleggaar FP, Schalm SW. Management of osteoporosis in primary biliary cirrhosis. Baillieres Clinical Gastroenterology 2000;14(4):629‐41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

