Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of MK-5046, a bombesin receptor subtype-3 (BRS-3) agonist, in healthy patients
- PMID: 22162541
- PMCID: PMC5137193
- DOI: 10.1177/0091270011419854
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of MK-5046, a bombesin receptor subtype-3 (BRS-3) agonist, in healthy patients
Abstract
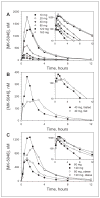
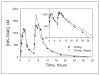
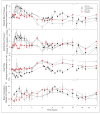
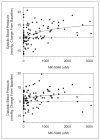
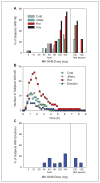
MK-5046 is an orally active, potent, selective agonist of the orphan G protein-coupled receptor bombesin receptor subtype-3 (BRS-3) that is under evaluation for treatment of obesity. We report the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of oral doses of MK-5046 (10-160 mg) in a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study in healthy and obese male volunteers. MK-5046 exposure increased dose proportionally, and MK-5046 was eliminated with an apparent terminal half-life of 1.5 to 3.5 hours. Single doses transiently increased blood pressure. Patients reported adverse events (erections and feeling hot, cold, and/or jittery) that coincided with time of occurrence (T(max)) and increased with increasing dose. No changes were observed in body temperature, heart rate, plasma glucose levels, or feelings of hunger/satiety. The blood pressure and thermal experiences attenuated with a second dose 6 hours after the first. Additionally, the erections suggest a possible, unanticipated, role for BRS-3 in reproductive physiology. Oral administration of MK-5046 achieves plasma concentrations that are projected to activate BRS-3 and therefore should be suitable for exploring its biological role in humans.
Figures
References
-
- Bray GA. Medical consequences of obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89(6):2583–2589. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. [September 7, 2011];Obesity and overweight. 2006 Available at: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/index.html.
-
- Sjostrom L, Lindroos AK, Peltonen M, et al. Lifestyle, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk factors 10 years after bariatric surgery. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(26):2683–2693. - PubMed
-
- Smith BR, Schauer P, Nguyen NT. Surgical approaches to the treatment of obesity: bariatric surgery. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2008;37(4):943–964. - PubMed
-
- Torgerson JS, Hauptman J, Boldrin MN, Sjostrom L. XENical in the prevention of diabetes in obese subjects (XENDOS) study: a randomized study of orlistat as an adjunct to lifestyle changes for the prevention of type 2 diabetes in obese patients. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(1):155–161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

