Comparison of the MALDI Biotyper system using Sepsityper specimen processing to routine microbiological methods for identification of bacteria from positive blood culture bottles
- PMID: 22162549
- PMCID: PMC3264150
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.05021-11
Comparison of the MALDI Biotyper system using Sepsityper specimen processing to routine microbiological methods for identification of bacteria from positive blood culture bottles
Abstract
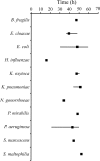
Bloodstream infections are a leading cause of admissions to hospital intensive care units and carry a high mortality rate. Clinical outcome can be greatly improved by early effective antibiotic therapy; therefore, broad-spectrum antimicrobial therapy is often initiated when there is a clinical suspicion of bloodstream infection. Unfortunately, this method may not always be effective when dealing with inherently resistant organisms and can also result in iatrogenic infection and the development of resistant isolates. Rapid identification of the infecting organism may aid in choosing appropriate antimicrobial therapy, thereby reducing these potential adverse events. We compared the matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) Biotyper system with Sepsityper specimen processing (Bruker Daltonics, Billerica, MA) to routine methods for the identification of microorganisms from 164 positive blood cultures. The MALDI Biotyper/Sepsityper identified 85.5% of bacterial isolates directly from positive monomicrobial blood cultures with 97.6% concordance to genus and 94.1% concordance to species with routine identification methods. Gram-negative isolates were more likely to produce acceptable confidence scores (97.8%) than gram-positive isolates (80.0%); however, genus and species concordance with routine identification methods were similar in both groups. Reanalysis of collected spectra using modified blood culture-specific parameters resulted in an improved overall identification rate for gram-positive bacteria (89.0%). Median times to identification using the MALDI Biotyper/Sepsityper were 23 to 83 h faster than routine methods for gram-positive isolates and 34 to 51 h faster for gram-negative isolates.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

