Effect of cutaneous blood flow on absorption of insulin: a methodological study in healthy male volunteers
- PMID: 22162782
- PMCID: PMC3230259
Effect of cutaneous blood flow on absorption of insulin: a methodological study in healthy male volunteers
Abstract
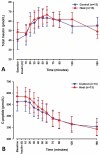
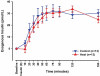
Absorption of drugs from subcutaneous tissue depends on several factors, including tissue perfusion at the administration site. Tissue perfusion can be manipulated by e.g. application of local heat. This may subsequently alter the rate or amount of absorption of drugs from a subcutaneous depot. The aim of the present study was to investigate if increased tissue perfusion after controlled local heating can change the absorption of subcutaneously administered short-acting insulin (Actrapid®, 100IU/ml). Thirteen healthy Caucasian males participated in two randomized experimental sessions; one session with locally applied controlled heat at the injection site, and a control session without local heat application. Tissue perfusion (blood flow) was monitored with Laser Doppler Imaging, and blood samples were taken to assess the levels of glucose and insulin. Local heat application at the site of insulin injection significantly enhanced tissue perfusion by approximately 145%. However, no correlation was found between insulin absorption and tissue perfusion. Based on our findings, it was concluded that tissue perfusion is not the rate-limiting factor in the absorption of high-concentration short-acting insulin from a subcutaneous depot. It is suggested that dissociation of insulin hexamers into dimers and monomers is a major rate limiting factor to the absorption.
Keywords: Actrapid®; Local heat; absorption; insulin; skin perfusion; subcutaneous depot.
Figures
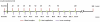



References
-
- Kimura T, Higaki K. Gastrointestinal transit and drug absorption. Biol Pharm Bull. 2002;25:149–164. - PubMed
-
- Woodley JF. Enzymatic barriers for GI peptide and protein delivery. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 1994;11:61–95. - PubMed
-
- Malik DK, Baboota S, Ahuja A, Hasan S, Ali J. Recent advances in protein and peptide drug delivery systems. Curr Drug Deliv. 2007;4:141–151. - PubMed
-
- Chen JW, Christiansen JS, Lauritzen T. Limitations to subcutaneous insulin administration in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2003;5:223–233. - PubMed
-
- Guerci B, Sauvanet JP. Subcutaneous insulinpharmacokinetic variability and glycemic variability. Diabetes Metab. 2005;31:4S7–4S24. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
