Evolutionary genetic dissection of human interferons
- PMID: 22162829
- PMCID: PMC3244034
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20111680
Evolutionary genetic dissection of human interferons
Abstract
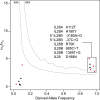
Interferons (IFNs) are cytokines that play a key role in innate and adaptive immune responses. Despite the large number of immunological studies of these molecules, the relative contributions of the numerous IFNs to human survival remain largely unknown. Here, we evaluated the extent to which natural selection has targeted the human IFNs and their receptors, to provide insight into the mechanisms that govern host defense in the natural setting. We found that some IFN-α subtypes, such as IFN-α6, IFN-α8, IFN-α13, and IFN-α14, as well as the type II IFN-γ, have evolved under strong purifying selection, attesting to their essential and nonredundant function in immunity to infection. Conversely, selective constraints have been relaxed for other type I IFNs, particularly for IFN-α10 and IFN-ε, which have accumulated missense or nonsense mutations at high frequencies within the population, suggesting redundancy in host defense. Finally, type III IFNs display geographically restricted signatures of positive selection in European and Asian populations, indicating that genetic variation at these genes has conferred a selective advantage to the host, most likely by increasing resistance to viral infection. Our population genetic analyses show that IFNs differ widely in their biological relevance, and highlight evolutionarily important determinants of host immune responsiveness.
Figures
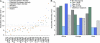



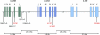
References
-
- Altshuler D.M., Gibbs R.A., Peltonen L., Altshuler D.M., Gibbs R.A., Peltonen L., Dermitzakis E., Schaffner S.F., Yu F., Peltonen L., et al. ; International HapMap 3 Consortium 2010. Integrating common and rare genetic variation in diverse human populations. Nature. 467:52–58 10.1038/nature09298 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

