Guanylate binding protein 1 is a novel effector of EGFR-driven invasion in glioblastoma
- PMID: 22162832
- PMCID: PMC3244036
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20111102
Guanylate binding protein 1 is a novel effector of EGFR-driven invasion in glioblastoma
Abstract
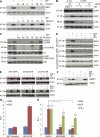
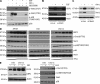
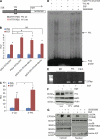
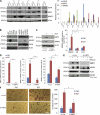
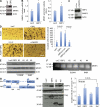
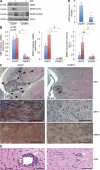
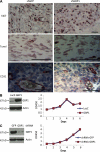
Although GBP1 (guanylate binding protein 1) was among the first interferon-inducible proteins identified, its function is still largely unknown. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) activation by amplification or mutation is one of the most frequent genetic lesions in a variety of human tumors. These include glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), which is characterized by independent but interrelated features of extensive invasion into normal brain parenchyma, rapid growth, necrosis, and angiogenesis. In this study, we show that EGFR activation promoted GBP1 expression in GBM cell lines through a signaling pathway involving Src and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Moreover, we identified YY1 (Yin Yang 1) as the downstream transcriptional regulator regulating EGFR-driven GBP1 expression. GBP1 was required for EGFR-mediated MMP1 (matrix metalloproteinase 1) expression and glioma cell invasion in vitro. Although deregulation of GBP1 expression did not affect glioma cell proliferation, overexpression of GBP1 enhanced glioma cell invasion through MMP1 induction, which required its C-terminal helical domain and was independent of its GTPase activity. Reducing GBP1 levels by RNA interference in invasive GBM cells also markedly inhibited their ability to infiltrate the brain parenchyma of mice. GBP1 expression was high and positively correlated with EGFR expression in human GBM tumors and cell lines, particularly those of the neural subtype. Together, these findings establish GBP1 as a previously unknown link between EGFR activity and MMP1 expression and nominate it as a novel potential therapeutic target for inhibiting GBM invasion.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Guanylate binding protein-1 mediates EGFRvIII and promotes glioblastoma growth in vivo but not in vitro.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 1;7(9):9680-91. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7109. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26848767 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of EGFR and EGFRvIII signaling networks in human glioblastoma tumor xenografts.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Dec;11(12):1724-40. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M112.019984. Epub 2012 Sep 10. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22964225 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of GBP1 predicts poor prognosis and promotes tumor growth in human glioblastoma multiforme.Cancer Biomark. 2019;25(3):275-290. doi: 10.3233/CBM-171177. Cancer Biomark. 2019. PMID: 29991124
-
MicroRNAs involved in the EGFR pathway in glioblastoma.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Feb;134:111115. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111115. Epub 2020 Dec 16. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33341046 Review.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor as a therapeutic target in glioblastoma.Neuromolecular Med. 2013 Jun;15(2):420-34. doi: 10.1007/s12017-013-8229-y. Epub 2013 Apr 11. Neuromolecular Med. 2013. PMID: 23575987 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA hypo-methylation and expression of GBP4 induces T cell exhaustion in pancreatic cancer.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024 Aug 7;73(10):208. doi: 10.1007/s00262-024-03786-3. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024. PMID: 39110249 Free PMC article.
-
A five-protein prognostic signature with GBP2 functioning in immune cell infiltration of clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023 Apr 17;21:2621-2630. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.04.015. eCollection 2023. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 38213893 Free PMC article.
-
Super enhancer loci of EGFR regulate EGFR variant 8 through enhancer RNA and strongly associate with survival in HNSCCs.Mol Genet Genomics. 2024 Jan 18;299(1):3. doi: 10.1007/s00438-023-02089-z. Mol Genet Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38236481
-
Guanylate-binding protein-1 is a potential new therapeutic target for triple-negative breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2017 Nov 7;17(1):727. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3726-2. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 29115931 Free PMC article.
-
HOXB7 promotes invasion and predicts survival in pancreatic adenocarcinoma.Cancer. 2013 Feb 1;119(3):529-39. doi: 10.1002/cncr.27725. Epub 2012 Aug 22. Cancer. 2013. PMID: 22914903 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angers-Loustau A., Hering R., Werbowetski T.E., Kaplan D.R., Del Maestro R.F. 2004. SRC regulates actin dynamics and invasion of malignant glial cells in three dimensions. Mol. Cancer Res. 2:595–605 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

