SUMO-SIM interactions regulate the activity of RGSZ2 proteins
- PMID: 22163035
- PMCID: PMC3232247
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028557
SUMO-SIM interactions regulate the activity of RGSZ2 proteins
Abstract
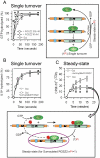
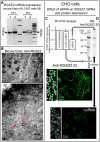
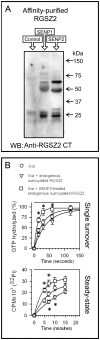
The RGSZ2 gene, a regulator of G protein signaling, has been implicated in cognition, Alzheimer's disease, panic disorder, schizophrenia and several human cancers. This 210 amino acid protein is a GTPase accelerating protein (GAP) on Gαi/o/z subunits, binds to the N terminal of neural nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) negatively regulating the production of nitric oxide, and binds to the histidine triad nucleotide-binding protein 1 at the C terminus of different G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). We now describe a novel regulatory mechanism of RGS GAP function through the covalent incorporation of Small Ubiquitin-like MOdifiers (SUMO) into RGSZ2 RGS box (RH) and the SUMO non covalent binding with SUMO-interacting motifs (SIM): one upstream of the RH and a second within this region. The covalent attachment of SUMO does not affect RGSZ2 binding to GPCR-activated GαGTP subunits but abolishes its GAP activity. By contrast, non-covalent binding of SUMO with RH SIM impedes RGSZ2 from interacting with GαGTP subunits. Binding of SUMO to the RGSZ2 SIM that lies outside the RH does not affect GαGTP binding or GAP activity, but it could lead to regulatory interactions with sumoylated proteins. Thus, sumoylation and SUMO-SIM interactions constitute a new regulatory mechanism of RGS GAP function and therefore of GPCR cell signaling as well.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Sumoylated RGS-Rz proteins act as scaffolds for Mu-opioid receptors and G-protein complexes in mouse brain.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2007 Apr;32(4):842-50. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1301184. Epub 2006 Aug 9. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2007. PMID: 16900103
-
The RGSZ2 protein exists in a complex with mu-opioid receptors and regulates the desensitizing capacity of Gz proteins.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005 Sep;30(9):1632-48. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300726. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005. PMID: 15827571
-
The Axonal Motor Neuropathy-Related HINT1 Protein Is a Zinc- and Calmodulin-Regulated Cysteine SUMO Protease.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019 Sep 1;31(7):503-520. doi: 10.1089/ars.2019.7724. Epub 2019 Jun 24. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019. PMID: 31088288 Free PMC article.
-
RGS17/RGSZ2 and the RZ/A family of regulators of G-protein signaling.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2006 Jun;17(3):390-9. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2006.04.001. Epub 2006 Apr 7. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2006. PMID: 16765607 Review.
-
SUMO Interacting Motifs: Structure and Function.Cells. 2021 Oct 21;10(11):2825. doi: 10.3390/cells10112825. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831049 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulator of G Protein Signaling 17 as a Negative Modulator of GPCR Signaling in Multiple Human Cancers.AAPS J. 2016 May;18(3):550-9. doi: 10.1208/s12248-016-9894-1. Epub 2016 Feb 29. AAPS J. 2016. PMID: 26928451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RGS17: an emerging therapeutic target for lung and prostate cancers.Future Med Chem. 2013 Jun;5(9):995-1007. doi: 10.4155/fmc.13.91. Future Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23734683 Free PMC article.
-
Estradiol accelerates the effects of fluoxetine on serotonin 1A receptor signaling.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2013 Jul;38(7):1145-57. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2012.11.005. Epub 2012 Dec 5. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2013. PMID: 23219224 Free PMC article.
-
Human HINT1 Mutant Proteins that Cause Axonal Motor Neuropathy Exhibit Anomalous Interactions with Partner Proteins.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Apr;58(4):1834-1845. doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-02265-x. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 33404983
-
The σ1 receptor engages the redox-regulated HINT1 protein to bring opioid analgesia under NMDA receptor negative control.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015 Apr 1;22(10):799-818. doi: 10.1089/ars.2014.5993. Epub 2015 Feb 18. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015. PMID: 25557043 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jordan JD, Carey KD, Stork PJ, Iyengar R. Modulation of rap activity by direct interaction of Galpha(o) with Rap1 GTPase-activating protein. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:21507–21510. - PubMed
-
- Mao H, Zhao Q, Daigle M, Ghahremani MH, Chidiac P, et al. RGS17/RGSZ2, a novel regulator of Gi/o, Gz, and Gq signaling. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:26314–26322. - PubMed
-
- Berman DM, Kozasa T, Gilman AG. The GTPase-activating protein RGS4 stabilizes the transition state for nucleotide hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:27209–27212. - PubMed
-
- Hunt TW, Fields TA, Casey PJ, Peralta EG. RGS10 is a selective activator of G alpha i GTPase activity. Nature. 1996;383:175–177. - PubMed
-
- Wang J, Tu Y, Woodson J, Song X, Ross EM. A GTPase-activating protein for the G protein Galphaz. Identification, purification, and mechanism of action. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:5732–5740. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

