Abnormal cholesterol is associated with prefrontal white matter abnormalities among obese adults, a diffusion tensor imaging study
- PMID: 22163070
- PMCID: PMC3234114
Abnormal cholesterol is associated with prefrontal white matter abnormalities among obese adults, a diffusion tensor imaging study
Abstract
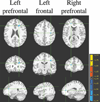
The brain is the most cholesterol-rich organ in the body. Although most of the cholesterol in the brain is produced endogenously, some studies suggest that systemic cholesterol may be able to enter the brain. We investigated whether abnormal cholesterol profiles correlated with diffusion-tensor-imaging-based estimates of white matter microstructural integrity of lean and overweight/obese (o/o) adults. Twenty-two lean and 39 obese adults underwent magnetic resonance imaging, kept a 3-day food diary, and had a standardized assessment of fasting blood lipids. The lean group ate less cholesterol rich food than o/o although both groups ate equivalent servings of food per day. Voxelwise correlational analyses controlling for age, diabetes, and white matter hyperintensities, resulted in two significant clusters of negative associations between abnormal cholesterol profile and fractional anisotropy, located in the left and right prefrontal lobes. When the groups were split, the lean subjects showed no associations, whereas the o/o group expanded the association to three significant clusters, still in the frontal lobes. These findings suggest that cholesterol profile abnormalities may explain some of the reductions in white matter microstructural integrity that are reported in obesity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Abnormal Cholesterol is Associated with Prefrontal White Matter Abnormalities among Obese Adults: a Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study.Neuroradiol J. 2011 Dec 30;24(6):854-61. doi: 10.1177/197140091102400604. Epub 2011 Dec 23. Neuroradiol J. 2011. PMID: 24059886
-
White matter integrity disparities between normal-weight and overweight/obese adolescents: an automated fiber quantification tractography study.Brain Imaging Behav. 2020 Feb;14(1):308-319. doi: 10.1007/s11682-019-00036-4. Brain Imaging Behav. 2020. PMID: 30719618
-
On the relation of white matter brain abnormalities and the asociality symptoms in schizophrenia outpatients - a DTI study.Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2021;81(1):80-95. doi: 10.21307/ane-2021-009. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2021. PMID: 33949167
-
Compromised white matter integrity in obesity.Obes Rev. 2015 Apr;16(4):273-81. doi: 10.1111/obr.12248. Epub 2015 Feb 10. Obes Rev. 2015. PMID: 25676886 Review.
-
White Matter Integrity Abnormalities in Healthy Overweight Individuals Revealed by Whole Brain Meta-Analysis of Diffusion Tensor Imaging Studies.J Obes. 2023 Oct 23;2023:7966540. doi: 10.1155/2023/7966540. eCollection 2023. J Obes. 2023. PMID: 37908490 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The oxysterol 27-hydroxycholesterol increases oxidative stress and regulate Nrf2 signaling pathway in astrocyte cells.Neurochem Res. 2015 Apr;40(4):758-66. doi: 10.1007/s11064-015-1524-2. Epub 2015 Jan 29. Neurochem Res. 2015. PMID: 25630716
-
Neuroimaging correlates of Alzheimer's disease biomarker concentrations in a racially diverse high-risk cohort of middle-aged adults.Alzheimers Dement. 2024 Sep;20(9):5961-5972. doi: 10.1002/alz.14051. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Alzheimers Dement. 2024. PMID: 39136298 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in brain changes between adults with childhood-onset epilepsy and controls: A prospective population-based study.Acta Neurol Scand. 2022 Mar;145(3):322-331. doi: 10.1111/ane.13560. Epub 2021 Nov 26. Acta Neurol Scand. 2022. PMID: 34837220 Free PMC article.
-
White Matter Microstructure Alterations in Older Adults With Dyslipidemia Associated With Cognitive and Locomotor Dysfunction Evaluated Using Neurite Orientation Dispersion and Density Imaging.Brain Behav. 2025 Jun;15(6):e70526. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70526. Brain Behav. 2025. PMID: 40437836 Free PMC article.
-
Bariatric Surgery Induces White and Grey Matter Density Recovery in the Morbidly Obese: A Voxel-Based Morphometric Study.Hum Brain Mapp. 2016 Nov;37(11):3745-3756. doi: 10.1002/hbm.23272. Hum Brain Mapp. 2016. PMID: 27400738 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bjorkhem I, Meaney S. Brain cholesterol: long secret life behind a barrier. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004 May;24(5):806–815. - PubMed
-
- Saito M, Benson EP, Rosenberg A. Metabolism of cholesterol and triacylglycerol in cultured chick neuronal cells, glial cells, and fibroblasts: accumulation of esterified cholesterol in serum-free culture. J Neurosci Res. 1987;18(2):319–325. - PubMed
-
- Snipes G, Suter U. In: Cholesterol and Myelin. R B, editor. New York: Plenum Press; 1998.
-
- Waelsch H, Sperry W, Stoyanoff VA. A study of the synthesis and deposition of lipids in brain and other tissues with deuterium as an indicator. J Biol Chem. 1940;135:291–296.
-
- Meaney S, Hassan M, Sakinis A, et al. Evidence that the major oxysterols in human circulation originate from distinct pools of cholesterol: a stable isotope study. J Lipid Res. 2001 Jan;42(1):70–78. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
