Neutralizing antibody response to hepatitis C virus
- PMID: 22163337
- PMCID: PMC3230844
- DOI: 10.3390/v3112127
Neutralizing antibody response to hepatitis C virus
Abstract
A critical first step in a "rational vaccine design" approach for hepatitis C virus (HCV) is to identify the most relevant mechanisms of immune protection. Emerging evidence provides support for a protective role of virus neutralizing antibodies, and the ability of the B cell response to modify the course of acute HCV infection. This has been made possible by the development of in vitro cell culture models, based on HCV retroviral pseudotype particles expressing E1E2 and infectious cell culture-derived HCV virions, and small animal models that are robust tools in studies of antibody-mediated virus neutralization. This review is focused on the immunogenic determinants on the E2 glycoprotein mediating virus neutralization and the pathways in which the virus is able to escape from immune containment. Encouraging findings from recent studies provide support for the existence of broadly neutralization antibodies that are not associated with virus escape. The identification of conserved epitopes mediating virus neutralization that are not associated with virus escape will facilitate the design of a vaccine immunogen capable of eliciting broadly neutralizing antibodies against this highly diverse virus.
Keywords: Hepatitis C virus; epitope; escape; neutralization antibodies; vaccine development.
Figures
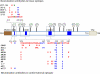
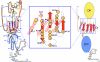
References
-
- World Health Organization Initiative for vaccine research. Hepatitis C. Available online: http://www.who.int/vaccine_research/diseases/viral_cancers/en/index2.html (accessed on 12 September 2011).
-
- Shepard C.W., Finelli L., Alter M.J. Global epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2005;5:558–567. - PubMed
-
- Pawlotsky J.M. The results of Phase III clinical trials with telaprevir and boceprevir presented at the Liver Meeting 2010: A new standard of care for hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection, but with issues still pending. Gastroenterology. 2011;140:746–754. - PubMed
-
- Pawlotsky J.M. Treatment failure and resistance with direct-acting antiviral drugs against hepatitis C virus. Hepatology. 2011;53:1742–1751. - PubMed
-
- Gerlach J.T., Diepolder H.M., Jung M.C., Gruener N.H., Schraut W.W., Zachoval R., Hoffmann R., Schirren C.A., Santantonio T., Pape G.R. Recurrence of hepatitis C virus after loss of virus-specific CD4(+) T-cell response in acute hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 1999;117:933–941. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

