Bioconjugation strategies for microtoroidal optical resonators
- PMID: 22163409
- PMCID: PMC3230978
- DOI: 10.3390/s101009317
Bioconjugation strategies for microtoroidal optical resonators
Abstract
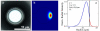
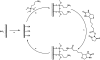
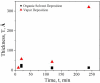
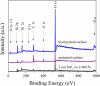
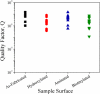
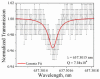
The development of label-free biosensors with high sensitivity and specificity is of significant interest for medical diagnostics and environmental monitoring, where rapid and real-time detection of antigens, bacteria, viruses, etc., is necessary. Optical resonant devices, which have very high sensitivity resulting from their low optical loss, are uniquely suited to sensing applications. However, previous research efforts in this area have focused on the development of the sensor itself. While device sensitivity is an important feature of a sensor, specificity is an equally, if not more, important performance parameter. Therefore, it is crucial to develop a covalent surface functionalization process, which also maintains the device's sensing capabilities or optical qualities. Here, we demonstrate a facile method to impart specificity to optical microcavities, without adversely impacting their optical performance. In this approach, we selectively functionalize the surface of the silica microtoroids with biotin, using amine-terminated silane coupling agents as linkers. The surface chemistry of these devices is demonstrated using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and fluorescent and optical microscopy. The quality factors of the surface functionalized devices are also characterized to determine the impact of the chemistry methods on the device sensitivity. The resulting devices show uniform surface coverage, with no microstructural damage. This work represents one of the first examples of non-physisorption-based bioconjugation of microtoroidal optical resonators.
Keywords: bioconjugation; high quality factor; optical resonators; sensors.
Figures




References
-
- Luppa PB, Sokoll LJ, Chan DW. Immunosensors—Principles and applications to clinical chemistry. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2001;314:1–26. - PubMed
-
- Ambrose WP, Goodwin PM, Jett JH, van Orden A, Werner JH, Keller RA. Single molecule fluorescence spectroscopy at ambient temperature. Chem. Rev. 1999;99:2929–2956. - PubMed
-
- Funatsu T, Harada Y, Higuchi H, Tokunaga M, Saito K, Ishii Y, Vale RD, Yanagida T. Imaging and nano-manipulation of single biomolecules. Biophys. Chem. 1997;68:63–72. - PubMed
-
- Wormke S, Mackowski S, Brotosudarmo THP, Jung C, Zumbusch A, Ehrl M, Scheer H, HofMann E, Hiller RG, Brauchle C. Monitoring fluorescence of individual chromophores in peridininchlorophyll-protein complex using single molecule spectroscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Bioenerg. 2007;1767:956–964. - PubMed
-
- Xie SN. Single-molecule approach to enzymology. Single Mol. 2001;2:229–236.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

