Detecting vital signs with wearable wireless sensors
- PMID: 22163501
- PMCID: PMC3231103
- DOI: 10.3390/s101210837
Detecting vital signs with wearable wireless sensors
Abstract
The emergence of wireless technologies and advancements in on-body sensor design can enable change in the conventional health-care system, replacing it with wearable health-care systems, centred on the individual. Wearable monitoring systems can provide continuous physiological data, as well as better information regarding the general health of individuals. Thus, such vital-sign monitoring systems will reduce health-care costs by disease prevention and enhance the quality of life with disease management. In this paper, recent progress in non-invasive monitoring technologies for chronic disease management is reviewed. In particular, devices and techniques for monitoring blood pressure, blood glucose levels, cardiac activity and respiratory activity are discussed; in addition, on-body propagation issues for multiple sensors are presented.
Keywords: BAN networks; RF sensing; on-body sensors; wearable sensors; wireless telemetry.
Figures

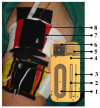



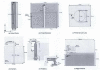

References
-
- Hall PS, Hao Y. Antennas and Propagation for Body-Centric Wireless Networks. 1st ed. Artech House; Boston, MA, USA: 2006.
-
- Hao Y, Foster R. Wireless body sensor networks for health-monitoring applications. Phys Meas. 2008;29:R27–R56. - PubMed
-
- Newman JD, Turner APF. Home blood glucose biosensors: A commercial perspective. Biosens Bioelectron. 2005;20:2435–2453. - PubMed
-
- Pickering TG, Shimbo D, Hass D. Ambulatory blood-pressure monitoring. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2368–2374. - PubMed
-
- Moranes JCTB, Cerulli M, Ng PS. A Strategy for Determination of Systolic, Mean and Diastolic Blood Pressures from Oscillometric Pulse Profiles. Proceedings of Computers in Cardiology 2000; Cambridge, MA, USA. September 24–27, 2000; pp. 211–214.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

