FLP/FRT recombination from yeast: application of a two gene cassette scheme as an inducible system in plants
- PMID: 22163670
- PMCID: PMC3231192
- DOI: 10.3390/s100908526
FLP/FRT recombination from yeast: application of a two gene cassette scheme as an inducible system in plants
Abstract
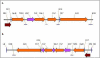
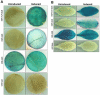
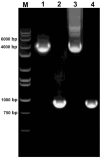
Phytosensors are plants that are genetically engineered for sensing and reporting the presence of a specific contaminant, including agriculturally important biological agents. Phytosensors are constructed by transforming plants to contain specific biotic- or abiotic-inducible promoters fused to a reporter gene. When such transgenic plants encounter the target biotic or abiotic agent, the specific inducible promoter is triggered and subsequently drives the expression of the reporter gene, which produces a signal for detection. However, several systems lack robustness, rapid induction and promoter strength. Here, we tested the FLP/FRT recombination system in a construct containing a two gene cassette organization and examined its potential in transgenic Arabidopsis and tobacco plants using a β-glucuronidase (GUS) reporter. In this model system, a heat-shock inducible promoter was employed to control the expression of the FLP recombinase gene. Upon heat induction and subsequent active FLP-mediated excision event, the GUS gene was placed in close proximity to the 35S promoter resulting in an active GUS reporter expression. Our results demonstrate that the two gene cassette scheme of inducible FLP/FRT recombination system is functional in tobacco and Arabidopsis, providing additional insights into its possible application in phytosensing such as creating strong readout capabilities.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; FLP/FRT; GUS reporter; heat shock; phytosensing; site-specific recombination; tobacco.
Figures

Similar articles
-
FLP recombinase in transgenic plants: constitutive activity in stably transformed tobacco and generation of marked cell clones in Arabidopsis.Plant J. 1995 Nov;8(5):637-52. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1995.08050637.x. Plant J. 1995. PMID: 8528276
-
Excision of selectable marker gene from transgenic tobacco using the GM-gene-deletor system regulated by a heat-inducible promoter.Biotechnol Lett. 2008 Jul;30(7):1295-302. doi: 10.1007/s10529-008-9684-7. Epub 2008 Mar 15. Biotechnol Lett. 2008. PMID: 18345518
-
Activity of the yeast FLP recombinase in Arabidopsis.Plant Mol Biol. 1995 Sep;28(6):1127-32. doi: 10.1007/BF00032673. Plant Mol Biol. 1995. PMID: 7548830
-
Targeted integration and removal of transgenes in hybrid aspen (Populus tremula L. x P. tremuloides Michx.) using site-specific recombination systems.Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2010 Mar;12(2):334-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1438-8677.2009.00293.x. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2010. PMID: 20398239 Review.
-
Generating mosaics for lineage analysis in flies.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2014 Jan-Feb;3(1):69-81. doi: 10.1002/wdev.122. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24902835 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficient clonal seeds sorting for apomictic hybrid rice using a pollen-specific gene switch system.Plant Biotechnol J. 2025 Jun;23(6):2266-2275. doi: 10.1111/pbi.70031. Epub 2025 Mar 19. Plant Biotechnol J. 2025. PMID: 40108776 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced genetic tools for plant biotechnology.Nat Rev Genet. 2013 Nov;14(11):781-93. doi: 10.1038/nrg3583. Epub 2013 Oct 9. Nat Rev Genet. 2013. PMID: 24105275 Review.
-
Heat-Shock-Induced Removal of Transgenes Using the Gene-Deletor System in Hybrid Aspen (Populus tremula × P. tremuloides).Genes (Basel). 2018 Oct 8;9(10):484. doi: 10.3390/genes9100484. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30297683 Free PMC article.
-
Transgene excision in pollen using a codon optimized serine resolvase CinH-RS2 site-specific recombination system.Plant Mol Biol. 2011 Apr;75(6):621-31. doi: 10.1007/s11103-011-9756-2. Epub 2011 Feb 26. Plant Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21359553
-
Excision of a selectable marker gene in transgenic banana using a Cre/lox system controlled by an embryo specific promoter.Plant Mol Biol. 2013 Sep;83(1-2):143-52. doi: 10.1007/s11103-013-0058-8. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Plant Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23591693
References
-
- Ferry N, Gatehouse AMR. Transgenic crop plants for resistance to biotic stress. In: Kole C, Michler CH, Abbott AG, Hall TC, editors. Transgenic Crop Plants. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2010. pp. 1–65.
-
- Gurr SJ, Rushton PJ. Engineering plants with increased disease resistance: How are we going to express it? Trend. Biotech. 2005;23:283–290. - PubMed
-
- Stewart CN., Jr Monitoring the presence and expression of transgenes in living plants. Trend. Plant Sci. 2005;10:390–396. - PubMed
-
- Stewart CN., Jr . Plant Biotechnology and Genetic: Principles, Techniques, and Applications. Wiley and Sons; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2008. pp. 1–416.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

