Development and evaluation of a miniaturized taste sensor chip
- PMID: 22163731
- PMCID: PMC3231247
- DOI: 10.3390/s111009878
Development and evaluation of a miniaturized taste sensor chip
Abstract
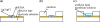
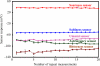
A miniaturized taste sensor chip was designed for use in a portable-type taste sensing system. The fabricated sensor chip (40 mm × 26 mm × 2.2 mm) has multiple taste-sensing sites consisting of a poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate) hydrogel with KCl as the electrolyte layer for stability of the membrane potential and artificial lipid membranes as the taste sensing elements. The sensor responses to the standard taste substances showed high accuracy and good reproducibility, which is comparable with the performance of the sensor probe of the commercialized taste sensing system. Thus, the fabricated taste sensor chip could be used as a key element for the realization of a portable-type taste sensing system.
Keywords: artificial lipid membrane; electrolyte layer; sensor chip; taste sensor.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Development of a portable taste sensor with a lipid/polymer membrane.Sensors (Basel). 2013 Jan 16;13(1):1076-84. doi: 10.3390/s130101076. Sensors (Basel). 2013. PMID: 23325168 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a sweetness sensor for aspartame, a positively charged high-potency sweetener.Sensors (Basel). 2014 Apr 23;14(4):7359-73. doi: 10.3390/s140407359. Sensors (Basel). 2014. PMID: 24763213 Free PMC article.
-
Miniaturized metal semiconductor metal photocurrent system for biomolecular sensing via chemiluminescence.Electrophoresis. 2009 Sep;30(18):3189-97. doi: 10.1002/elps.200900120. Electrophoresis. 2009. PMID: 19722206
-
Silicon Photonic Biosensors Using Label-Free Detection.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Oct 18;18(10):3519. doi: 10.3390/s18103519. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30340405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Taste Sensor: Electronic Tongue with Lipid Membranes.Anal Sci. 2020 Feb 10;36(2):147-159. doi: 10.2116/analsci.19R008. Epub 2019 Nov 29. Anal Sci. 2020. PMID: 31787669 Review.
Cited by
-
A High Sensitivity IDC-Electronic Tongue Using Dielectric/Sensing Membranes with Solvatochromic Dyes.Sensors (Basel). 2016 May 10;16(5):668. doi: 10.3390/s16050668. Sensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27171095 Free PMC article.
-
A 3D CFD Simulation and Analysis of Flow-Induced Forces on Polymer Piezoelectric Sensors in a Chinese Liquors Identification E-Nose.Sensors (Basel). 2016 Oct 20;16(10):1738. doi: 10.3390/s16101738. Sensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27775622 Free PMC article.
-
Soft and ion-conducting hydrogel artificial tongue for astringency perception.Sci Adv. 2020 Jun 5;6(23):eaba5785. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aba5785. eCollection 2020 Jun. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 32548269 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a portable taste sensor with a lipid/polymer membrane.Sensors (Basel). 2013 Jan 16;13(1):1076-84. doi: 10.3390/s130101076. Sensors (Basel). 2013. PMID: 23325168 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Bitterness-Sensing Systems.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Mar 23;13(4):414. doi: 10.3390/bios13040414. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37185489 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hayashi K, Yamanaka M, Toko K, Yamafuji K. Multichannel Taste Sensor Using Lipid Membranes. Sen. Actuat. B Chem. 1990;2:205–213.
-
- Toko K. Taste Sensor. Sen. Actuat. B Chem. 2000;64:205–215.
-
- Toko K. Biomimetic Sensor Technology. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK: 2000. pp. 113–180.
-
- Hayashi N, Chen R, Ikezaki H, Ujihara T. Evaluation of the Umami Taste Intensity of Green Tea by a Taste Sensor. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2008;56:7384–7387. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

