A surface plasmon resonance sensor for the detection of deoxynivalenol using a molecularly imprinted polymer
- PMID: 22164097
- PMCID: PMC3231472
- DOI: 10.3390/s110908654
A surface plasmon resonance sensor for the detection of deoxynivalenol using a molecularly imprinted polymer
Abstract
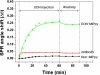
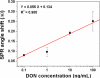
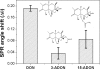
The aim of the present work was to investigate the feasibility of applying the molecular imprinting polymer technique to the detection of the mycotoxin deoxynivalenol (DON) using a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) transducer. A molecularly imprinted polypyrrole (MIPPy) film was prepared via electropolymerization of pyrrole onto a bare Au chip in the presence of a template DON molecule. Atomic force microscope SPR analysis showed that the MIPPy film was deposited homogeneously on the Au surface, with a thickness of 5 nm. The MIPPy-SPR sensor exhibited a linear response for the detection of DON in the range of 0.1-100 ng/mL (R2 = 0.988). The selectivity efficiency of the MIPPy film for DON and its acetylated analogs 3-ADON and 15-ADON was 100, 19, and 44%, respectively. The limit of detection for DON with the MIPPy-SPR for a standard solution was estimated at >1 ng/mL. These results suggest that the combination of SPR sensing with a MIPPy film as a synthetic receptor can be used to detect DON.
Keywords: deoxynivalenol; molecular imprinting polymer; polypyrrole; surface plasmon resonance; synthetic receptor.
Figures


References
-
- D’Mello JPF, Placinta CM, Macdonald AMC. Fusarium mycotoxins: A review of global implications for animal health, welfare and productivity. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 1999;80:183–205.
-
- Bullerman LB, Bianchini A. Stability of mycotoxins during food processing. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007;119:140–146. - PubMed
-
- Lancova K, Hajslova J, Kostelanska M, Kohoutkova J, Nedelnik J, Moravcova H, Vanova M. Fate of trichothecene mycotoxins during the processing: Milling and baking. Food Addit. Contam. 2008;25:650–659. - PubMed
-
- Rotter BA, Prelusky DB, Pestka JJ. Toxicology of desoxynivalenol (Vomitoxin) J. Toxicol Environ. Health. 1996;48:1–34. - PubMed
-
- Ehling G, Cockburn A, Snowdon P, Buchhaus H. The significance of the Fusarium toxin deoxynivalenol (DON) for human and animal health. Cereal Res. Commun. 1997;25:433–447.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

