Correlation of Local FOXP3-Expressing T Cells and Th1-Th2 Balance in Perennial Allergic Nasal Mucosa
- PMID: 22164170
- PMCID: PMC3227500
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/259867
Correlation of Local FOXP3-Expressing T Cells and Th1-Th2 Balance in Perennial Allergic Nasal Mucosa
Abstract
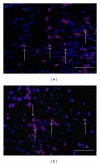
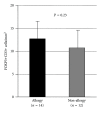
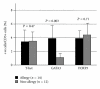
Regulatory T cells (Treg) play some important roles in allergic rhinitis. The most specific marker for Treg is FOXP3, a recently identified transcription factor that is essential for Treg development. In order to clarify the levels of Treg in allergic nasal mucosa, we studied the relationship between FOXP3-expressing cells and Th1-Th2 balance in nasal mucosa by means of immunohistochemistry. Human turbinates were obtained after turbinectomy from 26 patients (14 patients with perennial allergic rhinitis and 12 patients with nonallergic rhinitis). To identify the cells expressing the FOXP3 protein, double immunostaining was performed by using anti-FOXP3 antibody and anti-CD3 antibody. There was no significant difference in the percentage of FOXP3+CD3+ cells among CD3+ cells in the nasal mucosa of two groups. The proportion of FOXP3+CD3+ cells tend to be correlated positively with GATA3+CD3+ cells/T-bet+CD3+ cells ratio (R = 0.56, P = 0.04). A positive correlation with GATA3+CD3+/T-bet+CD3+ ratio and FOXP3+CD3+/CD3+ ratio suggests the role of local regulatory T cells as a minimal control of the chronic allergen exposure in nasal mucosa.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Derp1-modified dendritic cells attenuate allergic inflammation by regulating the development of T helper type1(Th1)/Th2 cells and regulatory T cells in a murine model of allergic rhinitis.Mol Immunol. 2017 Oct;90:172-181. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2017.07.015. Epub 2017 Aug 9. Mol Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28802126
-
Hydrogen-Rich Saline Ameliorates Allergic Rhinitis by Reversing the Imbalance of Th1/Th2 and Up-Regulation of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+Regulatory T Cells, Interleukin-10, and Membrane-Bound Transforming Growth Factor-β in Guinea Pigs.Inflammation. 2018 Feb;41(1):81-92. doi: 10.1007/s10753-017-0666-6. Inflammation. 2018. PMID: 28894978
-
Effects of pollen and nasal glucocorticoid on FOXP3+, GATA-3+ and T-bet+ cells in allergic rhinitis.Allergy. 2007 Sep;62(9):1007-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2007.01420.x. Allergy. 2007. PMID: 17686103 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of allergen-specific immunotherapy on functions of helper and regulatory T cells in patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis.Eur Cytokine Netw. 2011 Mar;22(1):15-23. doi: 10.1684/ecn.2011.0277. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2011. PMID: 21421451 Clinical Trial.
-
Regulatory-T, T-helper 1, and T-helper 2 cell differentiation in nasal mucosa of allergic rhinitis with olive pollen sensitivity.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2012;157(4):349-53. doi: 10.1159/000329159. Epub 2011 Nov 24. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22123238
Cited by
-
Exploration of Allergic Rhinitis: Epidemiology, Predisposing Factors, Clinical Manifestations, Laboratory Characteristics, and Emerging Pathogenic Mechanisms.Cureus. 2024 Oct 14;16(10):e71409. doi: 10.7759/cureus.71409. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39539885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-37 relieves allergic inflammation by inhibiting the CCL11 signaling pathway in a mouse model of allergic rhinitis.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Oct;20(4):3114-3121. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9078. Epub 2020 Jul 29. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32855679 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on allergic rhinitis in mice.Heliyon. 2024 Dec 19;11(1):e41340. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e41340. eCollection 2025 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39816505 Free PMC article.
-
HMSC-Derived Exosome Inhibited Th2 Cell Differentiation via Regulating miR-146a-5p/SERPINB2 Pathway.J Immunol Res. 2021 May 14;2021:6696525. doi: 10.1155/2021/6696525. eCollection 2021. J Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 34095322 Free PMC article.
-
Zonula occludens and nasal epithelial barrier integrity in allergic rhinitis.PeerJ. 2020 Sep 4;8:e9834. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9834. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32953271 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xu G, Mou Z, Jiang H, et al. A possible role of CD4+CD25+ T cells as well as transcription factor Foxp3 in the dysregulation of allergic rhinitis. Laryngoscope. 2007;117(5):876–880. - PubMed
-
- Lee SM, Gao B, Dahl M, Calhoun K, Fang D. Decreased FoxP3 gene expression in the nasal secretions from patients with allergic rhinitis. Otolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery. 2009;140(2):197–201. - PubMed
-
- Malmhäll C, Bossios A, Pullerits T, Lötvall J. Effects of pollen and nasal glucocorticoid on FOXP3+, GATA-3+ and T-bet+ cells in allergic rhinitis. Allergy: European Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2007;62(9):1007–1013. - PubMed
-
- Verhagen J, Akdis M, Traidl-Hoffmann C, et al. Absence of T-regulatory cell expression and function in atopic dermatitis skin. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2006;117(1):176–183. - PubMed
-
- Skrindo I. Experimentally induced accumulation of Foxp3+ T cells in upper airway allergy. Clinical and Experimental Allergy. 2011;41(7):954–962. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

