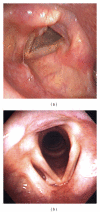
Endoscopic laryngeal findings in Japanese patients with laryngopharyngeal reflux symptoms
- PMID: 22164174
- PMCID: PMC3228393
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/908154
Endoscopic laryngeal findings in Japanese patients with laryngopharyngeal reflux symptoms
Abstract
Objective. To know the characteristics of endoscopic laryngeal and pharyngeal abnormalities in Japanese patients with laryngopharyngeal reflux symptoms (LPRS). Methods. A total of 146 endoscopic images of the larynx and pharynx (60 pairs for the rabeprazole group and 13 pairs for the control group) were presented to 15 otolaryngologists blinded to patient information and were scored according to several variables potentially associated with laryngopharyngeal reflux. The median value of the 15 scores for each item from each image was obtained. The mean pretreatment scores of each item and total score were assessed in both rabeprazole and control groups. In the rabeprazole group, the endoscopic findings before and after the 4-week treatment with rabeprazole were compared. Changes between corresponding duration in the control group were also evaluated. Results. The median and mean pretreatment total score was 3 and 3.02, respectively, from the 73 patients with LPRS. No significant differences were observed before and after treatment in either the rabeprazole or control groups for any item or total score. In 24 patients with a high pretreatment score (total score ≥ 4) from the rabeprazole group, significant decreases in scores for "thick endolaryngeal mucous" (0.54 to 0.17, P = 0.017) and total (4.77 to 3.58, P = 0.0003) were observed after the 4-week treatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rabeprazole is effective in treating laryngopharyngeal reflux in a randomized placebo-controlled trial.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010 Sep;8(9):770-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2010.03.009. Epub 2010 Mar 18. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. PMID: 20303417 Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation of upper abdominal symptoms using the Frequency Scale for the Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in patients with laryngopharyngeal reflux symptoms.J Gastroenterol. 2008;43(7):519-23. doi: 10.1007/s00535-008-2189-2. Epub 2008 Jul 23. J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18648738
-
Relationship between extralaryngeal endoscopic findings, proton pump inhibitor (PPI) response, and pH measures in suspected laryngopharyngeal reflux.Dis Esophagus. 2019 Apr 1;32(4):doy072. doi: 10.1093/dote/doy072. Dis Esophagus. 2019. PMID: 30101358
-
Abnormal endoscopic pharyngeal and laryngeal findings attributable to reflux.Am J Med. 2003 Aug 18;115 Suppl 3A:90S-96S. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(03)00204-3. Am J Med. 2003. PMID: 12928082 Review.
-
Evaluation and management of laryngopharyngeal reflux.JAMA. 2005 Sep 28;294(12):1534-40. doi: 10.1001/jama.294.12.1534. JAMA. 2005. PMID: 16189367 Review.
Cited by
-
Current perspectives on reflux laryngitis.Clin J Gastroenterol. 2014 Dec;7(6):471-5. doi: 10.1007/s12328-014-0535-x. Epub 2014 Nov 1. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25491904 Review.
-
Treatment of laryngopharyngeal reflux disease: A systematic review.World J Clin Cases. 2019 Oct 6;7(19):2995-3011. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i19.2995. World J Clin Cases. 2019. PMID: 31624747 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vakil N, van Zanten SV, Kahrilas P, et al. The Montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a global evidence-based consensus. American Journal of Gastroenterology. 2006;101(8):1900–1920. - PubMed
-
- Ford CN. Evaluation and management of laryngopharyngeal reflux. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2005;294(12):1534–1540. - PubMed
-
- Vaezi MF, Hicks DM, Abelson TI, Richter JE. Laryngeal signs and symptoms and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): a critical assessment of cause and effect association. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2003;1(5):333–344. - PubMed
-
- Branski RC, Bhattacharyya N, Shapiro J. The reliability of the assessment of endoscopic laryngeal findings associated with laryngopharyngeal reflux disease. Laryngoscope. 2002;112(6):1019–1024. - PubMed
-
- Belafsky PC, Postma GN, Koufman JA. The validity and reliability of the reflux finding score (RFS) Laryngoscope. 2001;111(8):1313–1317. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources