Juvenile angiofibroma: evolution of management
- PMID: 22164185
- PMCID: PMC3228400
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/412545
Juvenile angiofibroma: evolution of management
Abstract
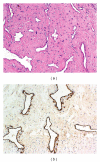
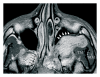
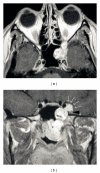
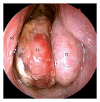
Juvenile angiofibroma is a rare benign lesion originating from the pterygopalatine fossa with distinctive epidemiologic features and growth patterns. The typical patient is an adolescent male with a clinical history of recurrent epistaxis and nasal obstruction. Although the use of nonsurgical therapies is described in the literature, surgery is currently considered the ideal treatment for juvenile angiofibroma. Refinement in preoperative embolization has provided significant reduction of complications and intraoperative bleeding with minimal risk of residual disease. During the last decade, an endoscopic technique has been extensively adopted as a valid alternative to external approaches in the management of small-intermediate size juvenile angiofibromas. Herein, we review the evolution in the management of juvenile angiofibroma with particular reference to recent advances in diagnosis and treatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endoscopic surgery for juvenile angiofibroma: when and how.Laryngoscope. 2003 May;113(5):775-82. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200305000-00003. Laryngoscope. 2003. PMID: 12792310
-
Endoscopic surgery for juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: where are the limits?Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006 Feb;14(1):1-5. doi: 10.1097/01.moo.0000188859.91607.65. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006. PMID: 16467630 Review.
-
Endonasal endoscopic management of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma without angiographic embolization.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013 Jul;270(7):2051-5. doi: 10.1007/s00405-012-2315-x. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013. PMID: 23271032
-
Case Report: Massive epistaxis from juvenile angiofibroma in an adolescent with severe haemophilia A.F1000Res. 2019 Sep 5;8:1593. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.20147.2. eCollection 2019. F1000Res. 2019. PMID: 31588357 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic resection of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma.Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 2012;73:132-6. doi: 10.1159/000334470. Epub 2012 Mar 29. Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 2012. PMID: 22472245 Review.
Cited by
-
The pterygopalatine fossa: imaging anatomy, communications, and pathology revisited.Insights Imaging. 2016 Aug;7(4):589-99. doi: 10.1007/s13244-016-0498-1. Epub 2016 May 26. Insights Imaging. 2016. PMID: 27230518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current approach of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: a case series.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2022 Jan-Mar;63(1):105-111. doi: 10.47162/RJME.63.1.10. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2022. PMID: 36074673 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudogenes in Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma: First Pilot Observation.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022 Oct;74(Suppl 2):1237-1241. doi: 10.1007/s12070-020-02336-4. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022. PMID: 36452697 Free PMC article.
-
Epistaxis as the initial presentation in a case of rheumatic heart disease.J Family Med Prim Care. 2018 Sep-Oct;7(5):1136-1138. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_211_18. J Family Med Prim Care. 2018. PMID: 30598978 Free PMC article.
-
Multiport Combined Endoscopic Approach to Nonembolized Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma with Parapharyngeal Extension: An Emerging Concept.Int J Otolaryngol. 2016;2016:4203160. doi: 10.1155/2016/4203160. Epub 2016 Dec 22. Int J Otolaryngol. 2016. PMID: 28101106 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lund VJ, Stammberger H, Nicolai P, et al. European position paper on endoscopic management of tumours of the nose, paranasal sinuses and skull base. Rhinology. Supplement. 2010;(22):1–143. - PubMed
-
- Chandler JR, Goulding R, Moskowitz L, Quencer RM. Nasopharyngeal angiofibromas: staging and management. Annals of Otology, Rhinology and Laryngology. 1984;93(4):322–329. - PubMed
-
- Glad H, Vainer B, Buchwald C, et al. Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibromas in Denmark 1981–2003: diagnosis, incidence, and treatment. Acta Oto-Laryngologica. 2007;127(3):292–299. - PubMed
-
- Maran AGD, Lund VJ. Nasal physiology. In: Maran AGD, Lund VJ, editors. Clinical Rhinology. Stuttgart, Germany: Georg Thieme; 1990. p. 5.
-
- Schuon R, Brieger J, Heinrich UR, Roth Y, Szyfter W, Mann WJ. Immunohistochemical analysis of growth mechanisms in juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology. 2007;264(4):389–394. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

