Modulation of calcium-dependent inactivation of L-type Ca2+ channels via β-adrenergic signaling in thalamocortical relay neurons
- PMID: 22164209
- PMCID: PMC3229489
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027474
Modulation of calcium-dependent inactivation of L-type Ca2+ channels via β-adrenergic signaling in thalamocortical relay neurons
Abstract
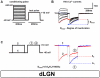
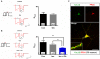
Neuronal high-voltage-activated (HVA) Ca(2+) channels are rapidly inactivated by a mechanism that is termed Ca(2+)-dependent inactivation (CDI). In this study we have shown that β-adrenergic receptor (βAR) stimulation inhibits CDI in rat thalamocortical (TC) relay neurons. This effect can be blocked by inhibition of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) with a cell-permeable inhibitor (myristoylated protein kinase inhibitor-(14-22)-amide) or A-kinase anchor protein (AKAP) St-Ht31 inhibitory peptide, suggesting a critical role of these molecules downstream of the receptor. Moreover, inhibition of protein phosphatases (PP) with okadaic acid revealed the involvement of phosphorylation events in modulation of CDI after βAR stimulation. Double fluorescence immunocytochemistry and pull down experiments further support the idea that modulation of CDI in TC neurons via βAR stimulation requires a protein complex consisting of Ca(V)1.2, PKA and proteins from the AKAP family. All together our data suggest that AKAPs mediate targeting of PKA to L-type Ca(2+) channels allowing their phosphorylation and thereby modulation of CDI.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




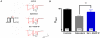

Similar articles
-
Ca2+/calcineurin-dependent inactivation of neuronal L-type Ca2+ channels requires priming by AKAP-anchored protein kinase A.Cell Rep. 2014 Jun 12;7(5):1410-1416. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.04.039. Epub 2014 May 15. Cell Rep. 2014. PMID: 24835998 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular Ca2+ release-dependent inactivation of Ca2+ currents in thalamocortical relay neurons.Eur J Neurosci. 2010 Feb;31(3):439-49. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07081.x. Epub 2010 Jan 25. Eur J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20105233
-
The A-kinase anchor protein MAP2B and cAMP-dependent protein kinase are associated with class C L-type calcium channels in neurons.J Biol Chem. 1999 Oct 15;274(42):30280-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.42.30280. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10514522
-
Regulation of phospholamban and troponin-I phosphorylation in the intact rat cardiomyocytes by adrenergic and cholinergic stimuli: roles of cyclic nucleotides, calcium, protein kinases and phosphatases and depolarization.Mol Cell Biochem. 1995 Aug-Sep;149-150:103-26. doi: 10.1007/BF01076569. Mol Cell Biochem. 1995. PMID: 8569720 Review.
-
Regulation of neuronal PKA signaling through AKAP targeting dynamics.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Jul;85(7):627-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.01.010. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16504338 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential effects of propranolol on head and upper limb tremor in patients with essential tremor and dystonia.J Neurol. 2018 Nov;265(11):2695-2703. doi: 10.1007/s00415-018-9052-z. Epub 2018 Sep 12. J Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30209649 Clinical Trial.
-
Noradrenaline Modulates the Membrane Potential and Holding Current of Medial Prefrontal Cortex Pyramidal Neurons via β1-Adrenergic Receptors and HCN Channels.Front Cell Neurosci. 2017 Nov 2;11:341. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00341. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29209170 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Propranolol on Motor Cortex Excitability in Essential Tremor: An Exploratory Study.Tremor Other Hyperkinet Mov (N Y). 2024 Jan 2;14:1. doi: 10.5334/tohm.829. eCollection 2024. Tremor Other Hyperkinet Mov (N Y). 2024. PMID: 38189055 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic modulation of spike timing-dependent calcium influx during corticostriatal upstates.J Neurophysiol. 2013 Oct;110(7):1631-45. doi: 10.1152/jn.00232.2013. Epub 2013 Jul 10. J Neurophysiol. 2013. PMID: 23843436 Free PMC article.
-
Ca2+/calcineurin-dependent inactivation of neuronal L-type Ca2+ channels requires priming by AKAP-anchored protein kinase A.Cell Rep. 2014 Jun 12;7(5):1410-1416. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.04.039. Epub 2014 May 15. Cell Rep. 2014. PMID: 24835998 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lacinova L. Voltage-dependent calcium channels. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2005;24(Suppl 1):1–78. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ, Lipp P, Bootman MD. The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000;1:11–21. - PubMed
-
- Budde T, Meuth S, Pape HC. Calcium-dependent inactivation of neuronal calcium channels. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2002;3:873–883. - PubMed
-
- Bardo S, Cavazzini MG, Emptage N. The role of the endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ store in the plasticity of central neurons. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2006;27:78–84. - PubMed
-
- Rankovic V, Ehling P, Coulon P, Landgraf P, Kreutz MR, et al. Intracellular Ca2+ release-dependent inactivation of Ca2+ currents in thalamocortical relay neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 2010;31:439–449. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

