Complex c-di-GMP signaling networks mediate transition between virulence properties and biofilm formation in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
- PMID: 22164276
- PMCID: PMC3229569
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028351
Complex c-di-GMP signaling networks mediate transition between virulence properties and biofilm formation in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
Abstract
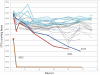
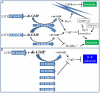
Upon Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection of the gut, an early line of defense is the gastrointestinal epithelium which senses the pathogen and intrusion along the epithelial barrier is one of the first events towards disease. Recently, we showed that high intracellular amounts of the secondary messenger c-di-GMP in S. typhimurium inhibited invasion and abolished induction of a pro-inflammatory immune response in the colonic epithelial cell line HT-29 suggesting regulation of transition between biofilm formation and virulence by c-di-GMP in the intestine. Here we show that highly complex c-di-GMP signaling networks consisting of distinct groups of c-di-GMP synthesizing and degrading proteins modulate the virulence phenotypes invasion, IL-8 production and in vivo colonization in the streptomycin-treated mouse model implying a spatial and timely modulation of virulence properties in S. typhimurium by c-di-GMP signaling. Inhibition of the invasion and IL-8 induction phenotype by c-di-GMP (partially) requires the major biofilm activator CsgD and/or BcsA, the synthase for the extracellular matrix component cellulose. Inhibition of the invasion phenotype is associated with inhibition of secretion of the type three secretion system effector protein SipA, which requires c-di-GMP metabolizing proteins, but not their catalytic activity. Our findings show that c-di-GMP signaling is at least equally important in the regulation of Salmonella-host interaction as in the regulation of biofilm formation at ambient temperature.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
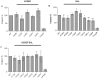
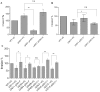

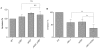
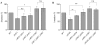
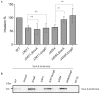
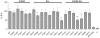
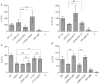
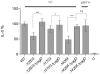
References
-
- Gerstel U, Römling U. Oxygen tension and nutrient starvation are major signals that regulate agfD promoter activity and expression of the multicellular morphotype in Salmonella typhimurium. Environ Microbiol. 2001;3:638–648. - PubMed
-
- Barak JD, Jahn CE, Gibson DL, Charkowski AO. The role of cellulose and O-antigen capsule in the colonization of plants by Salmonella enterica. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2007;20:1083–1091. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

