DNA electrophoretic migration patterns change after exposure of Jurkat cells to a single intense nanosecond electric pulse
- PMID: 22164287
- PMCID: PMC3229573
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028419
DNA electrophoretic migration patterns change after exposure of Jurkat cells to a single intense nanosecond electric pulse
Abstract
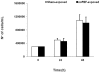
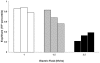
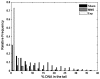
Intense nanosecond pulsed electric fields (nsPEFs) interact with cellular membranes and intracellular structures. Investigating how cells respond to nanosecond pulses is essential for a) development of biomedical applications of nsPEFs, including cancer therapy, and b) better understanding of the mechanisms underlying such bioelectrical effects. In this work, we explored relatively mild exposure conditions to provide insight into weak, reversible effects, laying a foundation for a better understanding of the interaction mechanisms and kinetics underlying nsPEF bio-effects. In particular, we report changes in the nucleus of Jurkat cells (human lymphoblastoid T cells) exposed to single pulses of 60 ns duration and 1.0, 1.5 and 2.5 MV/m amplitudes, which do not affect cell growth and viability. A dose-dependent reduction in alkaline comet-assayed DNA migration is observed immediately after nsPEF exposure, accompanied by permeabilization of the plasma membrane (YO-PRO-1 uptake). Comet assay profiles return to normal within 60 minutes after pulse delivery at the highest pulse amplitude tested, indicating that our exposure protocol affects the nucleus, modifying DNA electrophoretic migration patterns.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nanosecond pulsed electric fields (nsPEF) induce direct electric field effects and biological effects on human colon carcinoma cells.DNA Cell Biol. 2005 May;24(5):283-91. doi: 10.1089/dna.2005.24.283. DNA Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15869405
-
Diverse effects of nanosecond pulsed electric fields on cells and tissues.DNA Cell Biol. 2003 Dec;22(12):785-96. doi: 10.1089/104454903322624993. DNA Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 14683589
-
Long-lasting plasma membrane permeabilization in mammalian cells by nanosecond pulsed electric field (nsPEF).Bioelectromagnetics. 2007 Dec;28(8):655-63. doi: 10.1002/bem.20354. Bioelectromagnetics. 2007. PMID: 17654532
-
The Role of Pulse Repetition Rate in nsPEF-Induced Electroporation: A Biological and Numerical Investigation.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2015 Sep;62(9):2234-43. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2015.2419813. Epub 2015 Apr 3. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2015. PMID: 25850084
-
Microsecond and nanosecond electric pulses in cancer treatments.Bioelectromagnetics. 2012 Feb;33(2):106-23. doi: 10.1002/bem.20692. Epub 2011 Aug 3. Bioelectromagnetics. 2012. PMID: 21812011 Review.
Cited by
-
Electromagnetic fields act via activation of voltage-gated calcium channels to produce beneficial or adverse effects.J Cell Mol Med. 2013 Aug;17(8):958-65. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12088. Epub 2013 Jun 26. J Cell Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23802593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-thermal nanoelectroablation of UV-induced murine melanomas stimulates an immune response.Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012 Sep;25(5):618-29. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-148X.2012.01027.x. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012. PMID: 22686288 Free PMC article.
-
Nanosecond Electric Pulses Induce Early and Late Phases of DNA Damage and Cell Death in Cisplatin-Resistant Human Ovarian Cancer Cells.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Aug 8;2018:4504895. doi: 10.1155/2018/4504895. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30186858 Free PMC article.
-
Nanosecond Pulsed Electric Field Only Transiently Affects the Cellular and Molecular Processes of Leydig Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 18;22(20):11236. doi: 10.3390/ijms222011236. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681896 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Cytotoxic and Genotoxic Effects of Extremely Low-frequency Electromagnetic Field on Mesenchymal Stromal Cells.Glob Adv Health Med. 2018 May 18;7:2164956118777472. doi: 10.1177/2164956118777472. eCollection 2018. Glob Adv Health Med. 2018. PMID: 29796339 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Joshi RP, Schoenbach KH. Bioelectric effects of intense ultrashort pulses. Critical Reviews in Biomedical Engineering. 2010;38:255–304. - PubMed
-
- Vernier PT, Ziegler MJ, Sun Y, Gundersen MA, Tieleman P. Nanopore-facilitated, voltage-driven phosphatidylserine translocation in lipid bilayers—in cells and in silico. Phys. Biol. 2006a;3:233–247. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

