Eosinophilic esophagitis
- PMID: 22165816
- PMCID: PMC3245441
- DOI: 10.1186/1710-1492-7-S1-S8
Eosinophilic esophagitis
Abstract
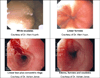
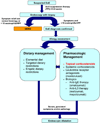
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is an atopic condition of the esophagus that has become increasingly recognized over the last decade. Diagnosis of the disorder is dependent on the patient's clinical manifestations and histologic findings on esophageal mucosal biopsies. Patients with eosinophilic esophagitis should be referred to both an allergist and gastroenterologist for optimal management, which may include dietary modifications, pharmacologic agents such as corticosteroids, leukotriene modifiers and biologics as well as mechanical dilatation of the esophagus. The epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of EoE are discussed in this review.
Figures
References
-
- Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Collins MH, Gupta SK, Justinich C, Putnam PE, Bonis P, Hassall E, Straumann A, Rothenberg ME. First International Gastrointestinal Eosinophil Research Symposium (FIGERS Subcommittees. Eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults: a systematic review and consensus recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:1342–1363. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.08.017. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ronkainen J, Talley NJ, Aro P, Storskrubb T, Johansson SE, Lind T, Bolling-Sternevald E, Vieth M, Stolte M, Walker MM, Agréus L. Prevalence of oesophageal eosinophils and eosinophilic oesophagitis in adults: the population-based Kalixanda study. Gut. 2007;56:615–620. doi: 10.1136/gut.2006.107714. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

