Regulation of urokinase expression at the posttranscription level by lung epithelial cells
- PMID: 22166006
- PMCID: PMC3254797
- DOI: 10.1021/bi201293x
Regulation of urokinase expression at the posttranscription level by lung epithelial cells
Abstract
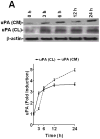
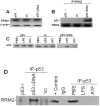
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) is expressed by lung epithelial cells and regulates fibrin turnover and epithelial cell viability. PMA, LPS, and TNF-alpha, as well as uPA itself, induce uPA expression in lung epithelial cells. PMA, LPS, and TNF-alpha induce uPA expression through increased synthesis as well as stabilization of uPA mRNA, while uPA increases its own expression solely through uPA mRNA stabilization. The mechanism by which lung epithelial cells regulate uPA expression at the level of mRNA stability is unclear. To elucidate this process, we sought to characterize protein-uPA mRNA interactions that regulate uPA expression. Regulation of uPA at the level of mRNA stability involves the interaction of a ~40 kDa cytoplasmic-nuclear shuttling protein with a 66 nt uPA mRNA 3'UTR sequence. We purified the uPA mRNA 3'UTR binding protein and identified it as ribonucleotide reductase M2 (RRM2). We expressed recombinant RRM2 and confirmed its interaction with a specific 66 nt uPA 3'UTR sequence. Immunoprecipitation of cell lysates with anti-RRM2 antibody and RT-PCR for uPA mRNA confirmed that RRM2 binds to uPA mRNA. Treatment of Beas2B cells with uPA or LPS attenuated RRM2-endogenous uPA mRNA interactions, while overexpression of RRM2 inhibited uPA protein and mRNA expression through destabilization of uPA mRNA. LPS exposure of lung epithelial cells translocates RRM2 from the cytoplasm to the nucleus in a time-dependent manner, leading to stabilization of uPA mRNA. This newly recognized pathway could influence uPA expression and a broad range of uPA-dependent functions in lung epithelial cells in the context of lung inflammation and repair.
Figures






References
-
- Dumler I, Petri T, Schleuning WD. Interaction of urokinase-type plasminogenactivator (u-PA) with its cellular receptor (u-PAR) induces phosphorylation on tyrosine of a 38 kda protein. FEBS Lett. 1993;322:37–40. - PubMed
-
- Shetty S, Pendurthi UR, Halady PK, Azghani AO, Idell S. Urokinase induces its own expression in Beas2b lung epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2002;283:L319–L328. - PubMed
-
- Koopman JL, Slomp J, de Bart AC, Quax PH, Verheijen JH. Effects of urokinase on melanoma cells are independent of high affinity binding to the urokinase receptor. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:33267–33272. - PubMed
-
- Koshelnick Y, Ehart M, Hufnagl P, Heinrich PC, Binder BR. Urokinase receptor is associated with the components of the JAK1/STAT1 signaling pathway and leads to activation of this pathway upon receptor clustering in the human kidney epithelial tumor cell line tcl-598. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:28563–28567. - PubMed
-
- Bhat GJ, Gunaje JJ, Idell S. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator induces tyrosine phosphorylation of a 78-kDa protein in H-157 cells. Am J Physiol. 1999;277:L301–L309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

