SProt: sphere-based protein structure similarity algorithm
- PMID: 22166105
- PMCID: PMC3289081
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-5956-9-S1-S20
SProt: sphere-based protein structure similarity algorithm
Abstract
Background: Similarity search in protein databases is one of the most essential issues in computational proteomics. With the growing number of experimentally resolved protein structures, the focus shifted from sequences to structures. The area of structure similarity forms a big challenge since even no standard definition of optimal structure similarity exists in the field.
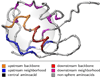
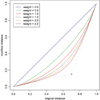
Results: We propose a protein structure similarity measure called SProt. SProt concentrates on high-quality modeling of local similarity in the process of feature extraction. SProt's features are based on spherical spatial neighborhood of amino acids where similarity can be well-defined. On top of the partial local similarities, global measure assessing similarity to a pair of protein structures is built. Finally, indexing is applied making the search process by an order of magnitude faster.
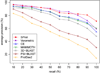
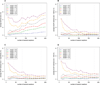
Conclusions: The proposed method outperforms other methods in classification accuracy on SCOP superfamily and fold level, while it is at least comparable to the best existing solutions in terms of precision-recall or quality of alignment.
Figures

References
-
- Kabsch W. A solution for the best rotation to relate two sets of vectors. Acta Crystallogr A. 1976;32(5):922–923. doi: 10.1107/S0567739476001873. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

