Presynaptic muscarinic M(2) receptors modulate glutamatergic transmission in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis
- PMID: 22166222
- PMCID: PMC3269526
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.11.013
Presynaptic muscarinic M(2) receptors modulate glutamatergic transmission in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis
Abstract
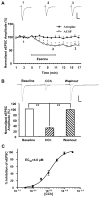
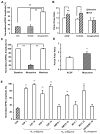
The anterolateral cell group of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST(ALG)) serves as an important relay station in stress circuitry. Limbic inputs to the BNST(ALG) are primarily glutamatergic and activity-dependent changes in this input have been implicated in abnormal behaviors associated with chronic stress and addiction. Significantly, local infusion of acetylcholine (ACh) receptor agonists into the BNST trigger stress-like cardiovascular responses, however, little is known about the effects of these agents on glutamatergic transmission in the BNST(ALG). Here, we show that glutamate- and ACh-containing fibers are found in close association in the BNST(ALG). Moreover, in the presence of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, eserine, endogenous ACh release evoked a long-lasting reduction of the amplitude of stimulus-evoked EPSCs. This effect was mimicked by exogenous application of the ACh analog, carbachol, which caused a reversible, dose-dependent, reduction of the evoked EPSC amplitude, and an increase in both the paired-pulse ratio and coefficient of variation, suggesting a presynaptic site of action. Uncoupling of postsynaptic G-proteins with intracellular GDP-β-S, or application of the nicotinic receptor antagonist, tubocurarine, failed to block the carbachol effect. In contrast, the carbachol effect was blocked by prior application of atropine or M(2) receptor-preferring antagonists, and was absent in M(2)/M(4) receptor knockout mice, suggesting that presynaptic M(2) receptors mediate the effect of ACh. Immunoelectron microscopy studies further revealed the presence of M(2) receptors on axon terminals that formed asymmetric synapses with BNST neurons. Our findings suggest that presynaptic M(2) receptors might be an important modulator of the stress circuit and hence a novel target for drug development.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures







References
-
- Adamec R. The relationship between the amygdala and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in the cat: an evoked potential and single cell study. Behav Neural Biol. 1989;52:295–320. - PubMed
-
- Alves FH, Crestani CC, Resstel LB, Correa FM. Cardiovascular effects of carbachol microinjected into the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis of the rat brain. Brain Res. 2007;1143:161–168. - PubMed
-
- Aoki C, Kabak S. Cholinergic terminals in the cat visual cortex: ultrastructural basis for interaction with glutamate-immunoreactive neurons and other cells. Vis Neurosci. 1992;8:177–191. - PubMed
-
- Bellingham MC, Berger AJ. Presynaptic depression of excitatory synaptic inputs to rat hypoglossal motoneurons by muscarinic M2 receptors. J Neurophysiol. 1996;76:3758–3770. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

