A pharmacologic inhibitor of the protease Taspase1 effectively inhibits breast and brain tumor growth
- PMID: 22166309
- PMCID: PMC3325786
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-2584
A pharmacologic inhibitor of the protease Taspase1 effectively inhibits breast and brain tumor growth
Abstract
The threonine endopeptidase Taspase1 has a critical role in cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis. In this study, we developed and evaluated small molecule inhibitors of Taspase1 as a new candidate class of therapeutic modalities. Genetic deletion of Taspase1 in the mouse produced no overt deficiencies, suggesting the possibility of a wide therapeutic index for use of Taspase1 inhibitors in cancers. We defined the peptidyl motifs recognized by Taspase1 and conducted a cell-based dual-fluorescent proteolytic screen of the National Cancer Institute diversity library to identify Taspase1 inhibitors (TASPIN). On the basis of secondary and tertiary screens the 4-[(4-arsonophenyl)methyl]phenyl] arsonic acid NSC48300 was determined to be the most specific active compound. Structure-activity relationship studies indicated a crucial role for the arsenic acid moiety in mediating Taspase1 inhibition. Additional fluorescence resonance energy transfer-based kinetic analysis characterized NSC48300 as a reversible, noncompetitive inhibitor of Taspase1 (K(i) = 4.22 μmol/L). In the MMTV-neu mouse model of breast cancer and the U251 xenograft model of brain cancer, NSC48300 produced effective tumor growth inhibition. Our results offer an initial preclinical proof-of-concept to develop TASPINs for cancer therapy.
©2011 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interests were disclosed.
Figures



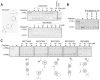


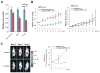
Comment in
-
Targeting Taspase1 for cancer therapy--letter.Cancer Res. 2012 Jun 1;72(11):2912; author reply 2913. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-0150. Epub 2012 May 16. Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22593195 No abstract available.
References
-
- Furie B, Furie BC. Molecular and cellular biology of blood coagulation. N Engl J Med. 1992;326:800–6. - PubMed
-
- Zaman MA, Oparil S, Calhoun DA. Drugs targeting the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2002;1:621–36. - PubMed
-
- Brown MS, Ye J, Rawson RB, Goldstein JL. Regulated intramembrane proteolysis: a control mechanism conserved from bacteria to humans. Cell. 2000;100:391–8. - PubMed
-
- Ye Y, Fortini ME. Proteolysis and developmental signal transduction. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2000;11:211–21. - PubMed
-
- Thornberry NA, Lazebnik Y. Caspases: enemies within. Science. 1998;281:1312–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

