Detection of nuclear and membrane antigens by liquid-based cytology following long-term storage of d1 cells, karpas cells, and peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- PMID: 22166505
- PMCID: PMC7370961
Detection of nuclear and membrane antigens by liquid-based cytology following long-term storage of d1 cells, karpas cells, and peripheral blood mononuclear cells
Abstract
Immunofluorescence is the most frequently utilized technique to analyze protein expression. Fixed immunofluorescent cell suspensions, however, can only be stored for a week. We investigated whether liquid-based cytology could be used to detect antigens in cultured cells after a long storage period. Murine and human cells were fixed in PreservCyt solution, stored for various periods, and then used to perform an automated immunocytochemical analysis. Phosphorylation of the nuclear transcription factor Stat-5 induced by IL-7 was detected up to 4 months after IL-7 stimulation. Simultaneous nuclear positivity for the proliferation index MIB-1 and membrane positivity for the CD30 antigen were evident three months after fixation. Liquid-based cytology thus ensures long-lasting nuclear and membrane antigen immunoreactivity and permits the storage of cells from laborious experiments at room temperature for future analyses.
Figures




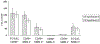
References
-
- Klinkhamer PJ, Meerding WJ, Rosier PF, Hanselaar AG. Liquid-based cervical cytology. Cancer 2003;99:263–271. - PubMed
-
- Bibbo M, Klump WJ, De Cecco J, Kovatich AJ. Procedure for immunocytochemical detection of P16INK4A antigen in thinlayer, liquid-based specimens. Acta Cytol 2002;46:25–29. - PubMed
-
- Zappacosta R, Caraceni D, Ciccocioppo L, Ottaviantonio M, Conti F, Andreozzi S, Petrucci F, Rosini S. Is HPV-DNA testing a useful tool in predicting low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion outcome? A retrospective longitudinal study. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 2010;23:317–326. - PubMed
-
- Kim K, Khaled AR, Reynolds D, Young HA, Lee CK, Durum SK. Characterization of an interleukin-7-dependent thymic cell line derived from a p53(−/−) mouse. J Immunol Methods 2003;274:177–184. - PubMed
-
- Grimley P M, Dong F, Rui H. Stat5a and Stat5b: fraternal twins of signal transduction and transcriptional activation. Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews 1999;10:131–157. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
