Effects of rose hip intake on risk markers of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease: a randomized, double-blind, cross-over investigation in obese persons
- PMID: 22166897
- PMCID: PMC3343291
- DOI: 10.1038/ejcn.2011.203
Effects of rose hip intake on risk markers of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease: a randomized, double-blind, cross-over investigation in obese persons
Abstract
Background/objectives: In studies performed in mice, rose hip powder has been shown to both prevent and reverse high-fat diet-induced obesity and glucose intolerance as well as reduce plasma levels of cholesterol. The aim of this study was to investigate whether daily intake of rose hip powder over 6 weeks exerts beneficial metabolic effects in obese individuals.
Subjects/methods: A total of 31 obese individuals with normal or impaired glucose tolerance were enrolled in a randomized, double-blind, cross-over study in which metabolic effects of daily intake of a rose hip powder drink over 6 weeks was compared with a control drink. Body weight, glucose tolerance, blood pressure, blood lipids and markers of inflammation were assessed in the subjects.
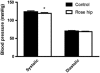
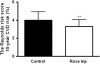
Results: In comparison with the control drink, 6 weeks of daily consumption of the rose hip drink resulted in a significant reduction of systolic blood pressure (-3.4%; P=0.021), total plasma cholesterol (-4.9%; P=0.0018), low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol (-6.0%; P=0.012) and LDL/HDL ratio (-6.5%; P=0.041). The Reynolds risk assessment score for cardiovascular disease was decreased in the rose hip group compared with the control group (-17%; P=0.007). Body weight, diastolic blood pressure, glucose tolerance, and plasma levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, triglycerides, incretins and markers of inflammation did not differ between the two groups.
Conclusions: Daily consumption of 40 g of rose hip powder for 6 weeks can significantly reduce cardiovascular risk in obese people through lowering of systolic blood pressure and plasma cholesterol levels.
Figures
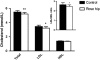
References
-
- Shaw JE, Sicree RA, Zimmet PZ. Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010;87:4–14. - PubMed
-
- Unger RH, Clark GO, Scherer PE, Orci L. Lipid homeostasis, lipotoxicity and the metabolic syndrome. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1801:209–214. - PubMed
-
- Cani PD, Delzenne NM. Interplay between obesity and associated metabolic disorders: new insights into the gut microbiota. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2009;9:737–743. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

