Incorporation of sentinel lymph node metastasis size into a nomogram predicting nonsentinel lymph node involvement in breast cancer patients with a positive sentinel lymph node
- PMID: 22167004
- PMCID: PMC4760742
- DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e318238f461
Incorporation of sentinel lymph node metastasis size into a nomogram predicting nonsentinel lymph node involvement in breast cancer patients with a positive sentinel lymph node
Abstract
Background and objective: Sentinel lymph node (SLN) metastasis size is an important predictor of non-SLN involvement. The goal of this study was to construct a nomogram incorporating SLN metastasis size to accurately predict non-SLN involvement in patients with SLN-positive disease.
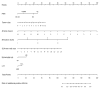
Methods: We identified 509 patients with invasive breast cancer with a positive SLN who underwent completion axillary lymph node dissection (ALND). Clinicopathologic data including age, tumor size, histology, grade, presence of multifocal disease, estrogen and progesterone receptor status, HER2/neu status, presence of lymphovascular invasion (LVI), number of SLN(s) identified, number of positive SLN(s), maximum SLN metastasis size and the presence of extranodal extension were recorded. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses identified factors predictive of positive non-SLNs. Using these variables, a nomogram was constructed and subsequently validated using an external cohort of 464 patients.
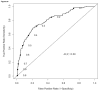
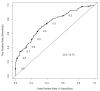
Results: On univariate analysis, the following factors were predictive of positive non-SLNs: number of SLN identified (P < 0.001), number of positive SLN (P < 0.001), SLN metastasis size (P < 0.001), extranodal extension (P < 0.001), tumor size (P = 0.001), LVI (P = 0.019), and histology (P = 0.034). On multivariate analysis, all factors remained significant except LVI. A nomogram was created using these variables (AUC = 0.80; 95% CI, 0.75-0.84). When applied to an external cohort, the nomogram was accurate and discriminating with an AUC = 0.74 (95% CI, 0.68-0.77).
Conclusion: SLN metastasis size is an important predictor for identifying non-SLN disease. In this study, we incorporated SLN metastasis size into a nomogram that accurately predicts the likelihood of having additional axillary metastasis and can assist in personalizing surgical management of breast cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Lucci A, McCall LM, Beitsch PD, et al. Surgical complications associated with sentinel lymph node dissection (SLND) plus axillary lymph node dissection compared with SLND alone in the American College of Surgeons Oncology Group Trial Z0011. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(24):3657–63. - PubMed
-
- Mansel RE, Fallowfield L, Kissin M, et al. Randomized multicenter trial of sentinel node biopsy versus standard axillary treatment in operable breast cancer: the ALMANAC Trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98(9):599–609. - PubMed
-
- Bolster MJ, Peer PG, Bult P, et al. Risk factors for non-sentinel lymph node metastases in patients with breast cancer. The outcome of a multi-institutional study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14(1):181–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

