Biosynthesis of proanthocyanidins in white clover flowers: cross talk within the flavonoid pathway
- PMID: 22167119
- PMCID: PMC3271758
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.111.189258
Biosynthesis of proanthocyanidins in white clover flowers: cross talk within the flavonoid pathway
Abstract
Proanthocyanidins and anthocyanins are produced by closely related branches of the flavonoid pathway and utilize the same metabolic intermediates. Previous studies have shown a flexible mechanism of flux diversion at the branch-point between the anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin pathways, but the molecular basis for this mechanism is poorly understood. Floral tissues in white clover plants (Trifolium repens) produce both proanthocyanidins and anthocyanins. This makes white clover amenable to studies of proanthocyanidin and anthocyanin biosynthesis and possible interactions within the flavonoid pathway. Results of this study show that the anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin pathways are spatially colocalized within epidermal cells of petals and temporally overlap in partially open flowers. A correlation between spatiotemporal patterns of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis with expression profiles of putative flavonoid-related genes indicates that these pathways may recruit different isoforms of flavonoid biosynthetic enzymes. Furthermore, in transgenic white clover plants with down-regulated expression of the anthocyanidin reductase gene, levels of flavan 3-ols, anthocyanins, and flavonol glycosides and the expression levels of a range of genes encoding putative flavonoid biosynthetic enzymes and transcription factors were altered. This is consistent with the hypothesis that flux through the flavonoid pathway may be at least partially regulated by the availability of intermediates.
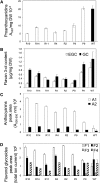
Figures





References
-
- Abrahams S, Lee E, Walker AR, Tanner GJ, Larkin PJ, Ashton AR. (2003) The Arabidopsis TDS4 gene encodes leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase (LDOX) and is essential for proanthocyanidin synthesis and vacuole development. Plant J 35: 624–636 - PubMed
-
- Almeida JR, D’Amico E, Preuss A, Carbone F, de Vos CH, Deiml B, Mourgues F, Perrotta G, Fischer TC, Bovy AG, et al. (2007) Characterization of major enzymes and genes involved in flavonoid and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis during fruit development in strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa). Arch Biochem Biophys 465: 61–71 - PubMed
-
- Baudry A, Heim MA, Dubreucq B, Caboche M, Weisshaar B, Lepiniec L. (2004) TT2, TT8, and TTG1 synergistically specify the expression of BANYULS and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 39: 366–380 - PubMed
-
- Beggs CJ, Kuhn K, Bocker R, Wellmann E. (1987) Phytochrome-induced flavonoid biosynthesis in mustard (Sinapis alba L.) cotyledons: enzymic control and differential regulation of anthocyanin and quercetin formation. Planta 172: 121–126 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

