Immune modulation during latent herpesvirus infection
- PMID: 22168421
- PMCID: PMC3243940
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01074.x
Immune modulation during latent herpesvirus infection
Abstract
Nearly all human beings, by the time they reach adolescence, are infected with multiple herpesviruses. At any given time, this family of viruses accounts for 35-40 billion human infections worldwide, making herpesviruses among the most prevalent pathogens known to exist. Compared to most other viruses, herpesviruses are also unique in that infection lasts the life of the host. Remarkably, despite their prevalence and persistence, little is known about how these viruses interact with their hosts, especially during the clinically asymptomatic phase of infection referred to as latency. This review explores data in human and animal systems that reveal the ability of latent herpesviruses to modulate the immune response to self and environmental antigens. From the perspective of the host, there are both potentially detrimental and surprisingly beneficial effects of this lifelong interaction. The realization that latent herpesvirus infection modulates immune responses in asymptomatic hosts forces us to reconsider what constitutes a 'normal' immune system in a healthy individual.
© 2011 John Wiley & Sons A/S.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors affirm that no conflicts of interest exist.
Figures
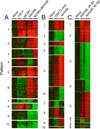
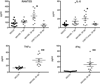
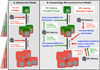

References
-
- Pellett PE, Roizman B. The Family Herpesviridae: A Brief Introduction. In: Knipe DM, Howely PM, editors. Fields Virology. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. pp. 2479–2500.
-
- Roizman B, Knipe DM, Whitley RJ. Herpes Simplex Viruses. In: Knipe DM, Howely PM, editors. Fields Virology. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. pp. 2501–2602.
-
- Rickinson AB, Kieff E. Epstein-Barr Virus. In: Knipe DM, Howely PM, editors. Fields Virology. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. pp. 2655–2700.
-
- Ganem D. Kapsoi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus. In: Knipe DM, Howely PM, editors. Fields Virology. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. pp. 2847–2888.
-
- Mocarski ES, Shenk T, Pass RF. Cytomegaloviruses. In: Knipe DM, Howely PM, editors. Fields Virology. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. pp. 2701–2772.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

