Vitamin D and cancer: a review of molecular mechanisms
- PMID: 22168439
- PMCID: PMC4572477
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20110744
Vitamin D and cancer: a review of molecular mechanisms
Abstract
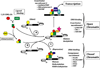
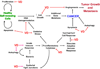
The population-based association between low vitamin D status and increased cancer risk can be inconsistent, but it is now generally accepted. These relationships link low serum 25OHD (25-hydroxyvitamin D) levels to cancer, whereas cell-based studies show that the metabolite 1,25(OH)2D (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D) is a biologically active metabolite that works through vitamin D receptor to regulate gene transcription. In the present review we discuss the literature relevant to the molecular events that may account for the beneficial impact of vitamin D on cancer prevention or treatment. These data show that although vitamin D-induced growth arrest and apoptosis of tumour cells or their non-neoplastic progenitors are plausible mechanisms, other chemoprotective mechanisms are also worthy of consideration. These alternative mechanisms include enhancing DNA repair, antioxidant protection and immunomodulation. In addition, other cell targets, such as the stromal cells, endothelial cells and cells of the immune system, may be regulated by 1,25(OH)2D and contribute to vitamin D-mediated cancer prevention.
Figures

References
-
- Fleet JC. In: In Calcium in Human Health. Weaver CM, Heaney RP, editors. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press; 2006. pp. 163–190.
-
- Garland CF, Garland FC. Do sunlight and vitamin D reduce the likelihood of colon cancer? Int.J.Epidemiol. 1980;9:227–231. - PubMed
-
- Grant WB, Mohr SB. Ecological studies of ultraviolet B, vitamin D and cancer since 2000. Ann Epidemiol. 2009;19:446–454. - PubMed
-
- Garland CF, Comstock GW, Garland FC, Helsing KJ, Shaw EK, Gorham ED. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and colon cancer: eight-year prospective study. Lancet. 1989;2:1176–1178. - PubMed
-
- Engel P, Fagherazzi G, Boutten A, Dupre T, Mesrine S, Boutron-Ruault MC, Clavel-Chapelon F. Serum 25(OH) vitamin D and risk of breast cancer: a nested case-control study from the French E3N cohort. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2010;19:2341–2350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

