Epileptic seizures from abnormal networks: why some seizures defy predictability
- PMID: 22169211
- PMCID: PMC3312991
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2011.11.006
Epileptic seizures from abnormal networks: why some seizures defy predictability
Abstract
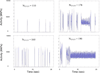
Seizure prediction has proven to be difficult in clinically realistic environments. Is it possible that fluctuations in cortical firing could influence the onset of seizures in an ictal zone? To test this, we have now used neural network simulations in a computational model of cortex having a total of 65,536 neurons with intercellular wiring patterned after histological data. A spatially distributed Poisson driven background input representing the activity of neighboring cortex affected 1% of the neurons. Gamma distributions were fit to the interbursting phase intervals, a non-parametric test for randomness was applied, and a dynamical systems analysis was performed to search for period-1 orbits in the intervals. The non-parametric analysis suggests that intervals are being drawn at random from their underlying joint distribution and the dynamical systems analysis is consistent with a nondeterministic dynamical interpretation of the generation of bursting phases. These results imply that in a region of cortex with abnormal connectivity analogous to a seizure focus, it is possible to initiate seizure activity with fluctuations of input from the surrounding cortical regions. These findings suggest one possibility for ictal generation from abnormal focal epileptic networks. This mechanism additionally could help explain the difficulty in predicting partial seizures in some patients.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors has any conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures





References
-
- Afra P, Jouny CC, Bergey GK. Duration of complex partial seizures: an intracranial EEG study. Epilepsia. 2008;49(4):677–684. - PubMed
-
- Andrzejak RG, Chicharro D, Elger CE, Mormann F. Seizure prediction: any better than chance? Clin Neurophysiol. 2009;120(8):1465–1478. - PubMed
-
- Arellano JI, Muñoz A, Ballesteros-Yáñez I, Sola RG, DeFelipe J. Histopathology and reorganization of chandelier cells in the human epileptic sclerotic hippocampus. Brain. 2004;127:45–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

