Randomized, placebo-controlled trials of antidepressants for acute major depression: thirty-year meta-analytic review
- PMID: 22169941
- PMCID: PMC3280655
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2011.306
Randomized, placebo-controlled trials of antidepressants for acute major depression: thirty-year meta-analytic review
Abstract
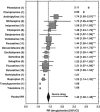
Antidepressant-placebo response-differences (RDs) in controlled trials have been declining, potentially confounding comparisons among older and newer drugs. For clinically employed antidepressants, we carried out a meta-analytic review of placebo-controlled trials in acute, unipolar, major depressive episodes reported over the past three decades to compare efficacy (drug-placebo RDs) of individual antidepressants and classes, and to consider factors associated with year-of-reporting by bivariate and multivariate regression modeling. Observed drug-placebo differences were moderate and generally similar among specific drugs, but larger among older antidepressants, notably tricyclics, than most newer agents. This outcome parallels selective increases in placebo-associated responses as trial-size has increased in recent years. Study findings generally support moderate efficacy of clinically employed antidepressants for acute major depression, but underscore limitations of meta-analyses of controlled trials for ranking drugs by efficacy. We suggest that efficiency and drug-placebo differences may be improved with fewer sites and subjects, and better quality-control of diagnostic and clinical assessments.
Figures

References
-
- Amsterdam JD. Double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of the safety and efficacy of selegiline transdermal system without dietary restrictions in patients with major depressive disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2003;64:208–214. - PubMed
-
- Anderson B. Methodological Errors in Medical Research: Incomplete Catalog. Blackwell: New York; 1990.
-
- Anderson IM. Meta-analytical studies on new antidepressants. Br Med Bull. 2001;57:161–178. - PubMed
-
- Andreoli V, Caillard V, Deo RS, Rybakowski JK, Versiani M. Reboxetine, new noradrenaline selective antidepressant, is at least as effective as fluoxetine in the treatment of depression. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2002;22:393–399. - PubMed
-
- Baldessarini RJ.2005Drug therapy of depression and anxiety disorders. Chapter 17In: Brunton LL, Lazo JS, Parker KL (eds).Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics11th edn.McGraw-Hill: New York; 429–459.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

