Bacterial magnetic particles as a novel and efficient gene vaccine delivery system
- PMID: 22170341
- PMCID: PMC3520014
- DOI: 10.1038/gt.2011.197
Bacterial magnetic particles as a novel and efficient gene vaccine delivery system
Abstract
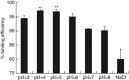
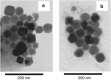
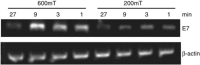
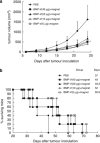
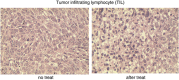
DNA vaccination is an attractive approach for eliciting antigen-specific immunity. In this study, we used magnetosomes (bacterial magnetic particles, BMPs) as carriers of a recombinant DNA composed of a secondary lymphoid tissue chemokine, human papillomavirus type E7 (HPV-E7) and Ig-Fc fragment (pSLC-E7-Fc) to generate a gene vaccine (BMP-V) for tumour immunotherapy. The results indicate that BMPs linked to DNA more efficiently in phosphate-buffered saline (pH=4-5) than in physiological saline. Efficient transfection of BMP-V in vitro and in vivo was achieved when a 600-mT static magnetic field was applied for 10 min. In a mouse tumour model, subcutaneous injection of BMP-V (5 μg, × 3 at 4-day intervals) plus magnetic exposure elicited systemic HPV-E7-specific immunity leading to significant tumour inhibition. The treated mice tolerated BMP-V immunisation well with no toxic side effects, as shown by histopathological examinations of major internal organs. Taken together, these results suggest that BMP can be used as a gene carrier to elicit a systemic immune response.
Figures






References
-
- Bansal A, Jackson B, West K, Wang S, Lu S, Kennedy JS, et al. Multifunctional T-cell characteristics induced by a polyvalent DNA prime/protein boost human immunodeficiency virus type 1 vaccine regimen given to healthy adults are dependent on the route and dose of administration. J Virol. 2008;8:6458–6469. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Donnelly J, Berry K, Ulmer JB. Technical and regulatory hurdles for DNA vaccines. Int J Parasitol. 2003;33:457–467. - PubMed
-
- Nicolas JF, Guy B. Intradermal, epidermal and transcutaneous vaccination: from immunology to clinical practice. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2008;7:1201–1214. - PubMed
-
- Bazylinski DA, Frankel RB. Magnetosome formation in prokaryotes. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2004;2:217–230. - PubMed
-
- Bazylinski DA, Garratt-Reed AR, Frankel B. Electron-microscopic studies of magnetosomes in magnetotactic bacteria. Microsc Res Techniq. 1994;27:389–401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

