A study of the use of impulse oscillometry in the evaluation of children with asthma: analysis of lung parameters, order effect, and utility compared with spirometry
- PMID: 22170806
- PMCID: PMC3423092
- DOI: 10.1002/ppul.21507
A study of the use of impulse oscillometry in the evaluation of children with asthma: analysis of lung parameters, order effect, and utility compared with spirometry
Abstract
Background: The ability to objectively measure lung function in children is critical in the assessment and treatment of asthma in this age group. We thus determined the effectiveness of impulse oscillometry (IOS) as a non-invasive technique to assess lung function in children and in comparison to spirometry for sensitivity and specificity, testing variability, and the order effect of sequential testing of IOS and spirometry.
Methods: One hundred seventeen children sequentially evaluated in a pediatric clinic and under medical care for disease, were asked to perform IOS and spirometry. The utility of IOS and spirometry in differentiating children that had asthma versus those children who did not was then analyzed.
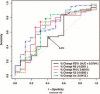
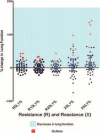
Results: In the primary analysis (n = 117), bronchodilator response using IOS distinguished asthmatics from non-asthmatics, P = 0.0008 for R10. Receiver-operator characteristic curve (ROC) analysis of R10 bronchodilator response at the best cut-off (-8.6% change) correctly identified 77% of patients with asthma and excluded 76% of non-asthmatics. Amongst those children able to perform spirometry (asthmatics, n = 66; non-asthmatics, n = 16), FEV(1) did not reveal a difference between these two groups, while area of reactance (AX) did distinguish these groups (P = 0.0092). Sequential testing of IOS and then spirometry (n = 47) showed a significant decrement in lung function as determined by IOS following performance of spirometry (P = 0.0309).
Conclusion: In the diagnosis and management of children with lung disease, IOS is a non-invasive approach that easily and objectively measures lung impedance and should be considered as both an adjunct, and in some situations, an alternative to standard spirometry.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
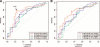
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic value of spirometry vs impulse oscillometry: A comparative study in children with sickle cell disease.Pediatr Pulmonol. 2019 Sep;54(9):1422-1430. doi: 10.1002/ppul.24382. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2019. PMID: 31211524
-
Impulse oscillometry in acute and stable asthmatic children: a comparison with spirometry.J Asthma. 2016;53(2):179-86. doi: 10.3109/02770903.2015.1081699. Epub 2015 Sep 14. J Asthma. 2016. PMID: 26367097
-
Impulse oscillometry provides an effective measure of lung dysfunction in 4-year-old children at risk for persistent asthma.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003 Aug;112(2):317-22. doi: 10.1067/mai.2003.1627. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12897737
-
Computer-aided classification of small airways dysfunction using impulse oscillometric features: a children-focused review.Biomed Tech (Berl). 2020 Apr 28;65(2):121-131. doi: 10.1515/bmt-2018-0219. Biomed Tech (Berl). 2020. PMID: 31600137 Review.
-
Impulse oscillometry in the assessment of children's lung function.Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2019 May-Jun;47(3):295-302. doi: 10.1016/j.aller.2018.03.003. Epub 2018 Jul 5. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2019. PMID: 29983239 Review.
Cited by
-
Impulse oscillometry reference values and bronchodilator response in three- to five-year old children living at high altitude.J Asthma Allergy. 2019 Sep 19;12:263-271. doi: 10.2147/JAA.S214297. eCollection 2019. J Asthma Allergy. 2019. PMID: 31571933 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Bedroom Particulate Matter Filtration and Changes in Airway Pathophysiology in Children With Asthma.JAMA Pediatr. 2020 Jun 1;174(6):533-542. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.0140. JAMA Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32250418 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Assessment of airway reversibility in asthmatic children using forced oscillation technique - A single-center experience from North India.Lung India. 2021 May-Jun;38(3):229-235. doi: 10.4103/lungindia.lungindia_354_20. Lung India. 2021. PMID: 33942746 Free PMC article.
-
Bronchodilator Response Assessed by the Forced Oscillation Technique Identifies Poor Asthma Control With Greater Sensitivity Than Spirometry.Chest. 2020 Jun;157(6):1435-1441. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.12.035. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Chest. 2020. PMID: 31982392 Free PMC article.
-
Impulse oscillometry system for assessing small airway dysfunction in pediatric bronchiolitis obliterans; association with conventional pulmonary function tests.PLoS One. 2023 Feb 7;18(2):e0280309. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280309. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36749747 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Foliaki S, Annesi-Maesano I, Daniel R, Fakakovikaetau T, Magatongia M, Tuuau-Potoi N, Waqatakirewa L, Cheng SK, Pearce N. Prevalence of symptoms of childhood asthma, allergic rhino-conjunctivitis and eczema in the Pacific: the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC). Allergy. 2007;62:259–264. - PubMed
-
- Expert Panel Report 3 (EPR-3): Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma-Summary Report 2007. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;120:S94–S138. - PubMed
-
- Finkelstein JA, Lozano P, Shulruff R, Inui TS, Soumerai SB, Ng M, Weiss KB. Self-reported physician practices for children with asthma: are national guidelines followed? Pediatrics. 2000;106:886–896. - PubMed
-
- Stanojevic S, Wade A, Cole TJ, Lum S, Custovic A, Silverman M, Hall GL, Welsh L, Kirkby J, Nystad W, Badier M, Davis S, Turner S, Piccioni P, Vilozni D, Eigen H, Vlachos-Mayer H, Zheng J, Tomalak W, Jones M, Hankinson JL, Stocks J. Spirometry centile charts for young Caucasian children: the Asthma UK Collaborative Initiative. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;180:547–552. - PubMed
-
- Goldman MD. Clinical application of forced oscillation. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2001;14:341–350. - PubMed

