Comparison of HIV-1 RNA measurements obtained by using plasma and dried blood spots in the automated abbott real-time viral load assay
- PMID: 22170904
- PMCID: PMC3295109
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00418-11
Comparison of HIV-1 RNA measurements obtained by using plasma and dried blood spots in the automated abbott real-time viral load assay
Abstract
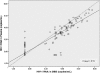
Dried blood spots (DBS) may be a promising alternative specimen type to plasma for measuring the viral load (VL) in HIV-infected individuals in resource-limited settings. However, characterization of assay performance using DBS is incomplete. In this prospective study, the VL was measured in parallel using plasma and DBS specimens collected at the same time from 157 HIV-1-infected individuals. DBS were prepared by dispensing 50 μl of blood onto filter paper cards and were stored desiccated at -20°C. Nucleic acid extraction from plasma and DBS was performed automatically using the Abbott m2000sp instrument, and the VL was measured using the RealTime HIV-1 VL assay, which has a lower limit of detection of 40 HIV RNA copies/ml. The correlation between plasma and DBS results was good (R = 0.91; P < 0.001). The mean difference in the VL (DBS minus plasma) was 0.35 log copies (standard deviation [SD], 0.47 log copies). A total of 40 (26%) paired specimens had a difference of >0.5 log copy, and in 12 (7.8%) it was >1 log copy. the VL from DBS was measurable in 95.7% of specimens with a plasma VL of >2.74 log copies (550 HIV RNA copies/ml). In summary, the VL can reliably be measured using DBS with the Abbott RealTime HIV-1 assay. The estimated lower limit of detection of this automated methodology on DBS is 550 copies/ml, a threshold that may be acceptable for periodic VL monitoring in patients on antiretroviral therapy in resource-limited settings, where early detection of virologic treatment failure is often problematic.
Figures

References
-
- Alvarez-Muñoz MT, et al. 2005. High correlation of human immunodeficiency virus type-1 viral load measured in dried-blood spot samples and in plasma under different storage conditions. Arch. Med. Res. 36:382–386 - PubMed
-
- Amellal B, Katlama C, Calvez V. 2007. Evaluation of the use of dried spots and of different storage conditions of plasma for HIV-1 RNA quantification. HIV Med. 8:396–400 - PubMed
-
- Andreotti M, et al. 2010. Correlation between HIV-1 viral load quantification in plasma, dried blood spots, and dried plasma spots using the Roche COBAS Taqman assay. J. Clin. Virol. 47:4–7 - PubMed
-
- Bertagnolio S, et al. 2007. HIV-1 drug resistance surveillance using dried whole blood spots. Antivir. Ther. 12:107–113 - PubMed
-
- Bertagnolio S, et al. 2010. Dried blood spots for HIV-1 drug resistance and viral load testing: a review of current knowledge and WHO efforts for global HIV drug resistance surveillance. AIDS Rev. 12:195–208 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

